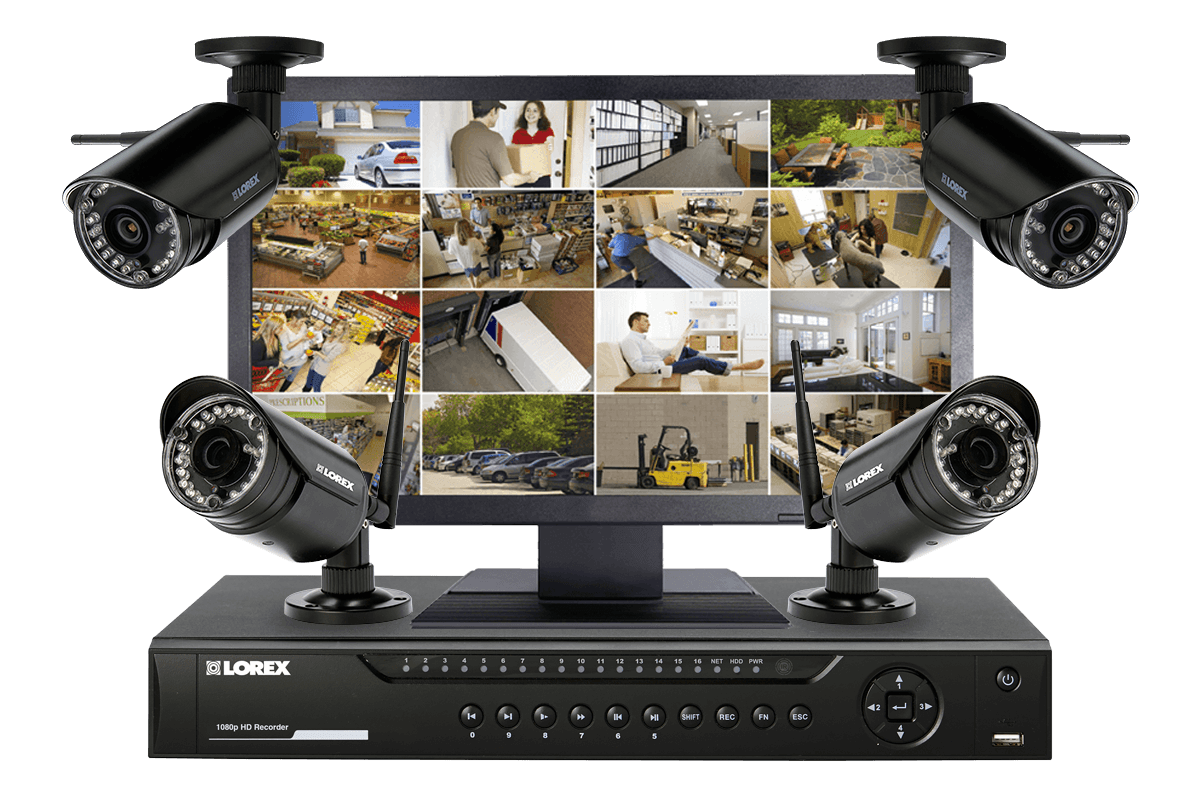
Introducing the commercial camera security system, your ultimate solution for safeguarding your business premises. In today’s fast-paced world, ensuring the security of your assets has never been more critical. With cutting-edge technology and advanced features, these systems offer unparalleled surveillance that keeps your property safe around the clock.
From high-definition video quality to remote access capabilities, commercial camera security systems are designed to meet the diverse needs of businesses. They not only deter potential threats but also provide valuable evidence when needed, making them an essential investment for any organization concerned about safety and security.
Are you tired of spending your precious weekends scrubbing floors and fighting dust bunnies? Do you dream of a cleaner home without the hassle of traditional cleaning methods? Introducing the UltraClean 3000, the unparalleled solution that will revolutionize the way you clean!
Why Choose the UltraClean 3000?
The UltraClean 3000 is not just another cleaning device; it’s a complete cleaning revolution! Combining cutting-edge technology with user-friendly design, this state-of-the-art cleaning system is engineered specifically for busy individuals and families who deserve a spotless home without sacrificing their free time.
Features You’ll Love!
- Smart Sensor Technology: The UltraClean 3000 features advanced sensor technology that detects dirt and adjusts cleaning power accordingly. Say goodbye to missed spots!
- Self-Cleaning Mechanism: This innovative feature automatically cleans the machine after each use, ensuring optimal performance every time.
- Eco-Friendly Cleaning: The UltraClean 3000 uses biodegradable cleaning solutions, making it safe for your family and the environment.
- Whisper-Quiet Operation: Enjoy a peaceful home while the UltraClean 3000 operates quietly in the background.
- Multi-Surface Compatibility: Whether it’s hardwood, tile, or carpet, the UltraClean 3000 can tackle it all!
How Does It Work?
Operating the UltraClean 3000 is as easy as pressing a button! Simply select your desired cleaning mode, and let the device take care of the rest. Its intelligent mapping system enables the UltraClean 3000 to navigate around furniture and obstacles, ensuring every corner of your home is thoroughly cleaned.
Step-By-Step Cleaning Process:
- Set It Up: Place the UltraClean 3000 in the center of the room, plug it in, and connect it to the app on your smartphone.
- Choose Your Cleaning Mode: Select from various modes tailored to your needs – from deep cleaning to quick touch-ups.
- Let It Work: Sit back, relax, and enjoy your free time while the UltraClean 3000 does the heavy lifting!
- Automatic Return: Once finished, the device will return to its charging station, ready for its next cleaning session.
Testimonials from Happy Customers!
“The UltraClean 3000 has changed my life! I can finally spend my weekends enjoying time with my family instead of cleaning. It’s like having a personal maid!”
– Sarah T.
“I was amazed at how much dust and dirt was collected after just one use. The self-cleaning feature is a game-changer!”
– James L.
“I love that it’s eco-friendly! I can clean my home without worrying about harmful chemicals around my kids and pets.”
– Emily R.
Special Offer Just for You!
For a limited time, purchase the UltraClean 3000 and receive a 20% discount plus free shipping! That’s right, for just $399.99, you can transform your cleaning routine. Don’t miss out on this incredible offer!
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I use the UltraClean 3000?
For optimal results, we recommend using the UltraClean 3000 at least twice a week. However, feel free to use it as often as you like!
Can the UltraClean 3000 handle pet hair?
Absolutely! The UltraClean 3000 is specifically designed to pick up pet hair and dander, making it perfect for pet owners.
Is the cleaning solution included?
Yes, your purchase includes a starter pack of our eco-friendly cleaning solution. Additional refills are available for purchase.

Join the Cleaning Revolution Today!
Don’t let dirt and dust take over your life. With the UltraClean 3000, you’ll reclaim your time while enjoying a cleaner, healthier home. Join the countless satisfied customers who have made the switch to effortless cleaning!
Order now and experience the future of home cleaning. The only thing you’ll regret is not getting it sooner!
Contact Us
If you have any questions or need assistance, our friendly customer service team is here to help! Reach out to us at support@ultraclean3000.com or call us at 1-800-555-0199.
Follow Us on Social Media!
Stay updated on the latest tips, tricks, and deals by following us on social media:
Don’t wait! Clean less, live more with the UltraClean 3000 today!
Answers to Common Questions
How long does a commercial camera security system last?

Typically, a well-maintained commercial camera security system can last between 5 to 10 years.
Can I access my commercial camera security system remotely?
Yes, most modern systems offer remote access through smartphones and computers for real-time monitoring.
What is the installation process for a commercial camera security system?
The installation usually involves site assessment, equipment setup, and configuration, which can be completed by professionals or DIY.
Are commercial camera security systems expensive?
Costs can vary widely based on features, but there are options available for various budgets.
Do these systems require regular maintenance?

Yes, periodic maintenance is recommended to ensure optimal performance and longevity.