Microsoft re releases exchange server security update – Microsoft re-releases Exchange Server security update—and this isn’t just another patch. This crucial update tackles serious vulnerabilities, impacting everything from small businesses to global corporations. We’re diving deep into what’s new, who’s affected, and how to secure your systems before it’s too late. Think of it as your ultimate guide to navigating this critical security landscape, complete with practical steps and real-world scenarios.
This re-release isn’t just a minor tweak; it addresses previously unknown weaknesses that could leave your data vulnerable. We’ll break down the specifics of these vulnerabilities, the differences between this update and its predecessors, and the best ways to implement it smoothly, minimizing disruption to your workflow. We’ll also explore the potential consequences of ignoring this update—trust us, you don’t want to find out the hard way.
The Nature of the Re-released Exchange Server Security Update
Source: pcdn.co
Microsoft’s re-released Exchange Server security update addresses critical vulnerabilities that were previously patched, but with some lingering issues. This isn’t just a simple re-patch; it’s a refined approach to tackling persistent security risks, ensuring a more robust and secure environment for Exchange Server users. This update focuses on strengthening existing defenses and improving the overall patching process.
This re-released update specifically targets vulnerabilities that allowed malicious actors to exploit weaknesses in the Exchange Server’s architecture, leading to potential data breaches and system compromises. Previous patches, while addressing the initial vulnerabilities, inadvertently introduced unforeseen complications or left some loopholes open. This latest release aims to resolve these lingering issues, providing a more comprehensive solution. The specific vulnerabilities addressed include improved protection against ProxyShell, ProxyLogon, and other previously known exploits. The differences lie in the enhanced code stability and improved compatibility with various Exchange Server versions and configurations.
Vulnerabilities Addressed and Differences from Previous Versions
The re-released update focuses on strengthening several aspects of Exchange Server security. Previous updates primarily addressed the initial exploitation vectors, such as those leveraged in ProxyShell and ProxyLogon attacks. However, these initial patches left some systems vulnerable to alternative attack methods or experienced unexpected side effects, such as service disruptions. This new release includes not only refined code to eliminate these vulnerabilities but also incorporates improvements to error handling and overall system stability. It aims to be a more comprehensive fix, addressing both the original vulnerabilities and subsequent weaknesses that were uncovered. For example, one significant improvement is the enhanced validation of client requests, making it much harder for attackers to bypass security measures.
Patching Methods Comparison
Previous updates often relied on a single cumulative update package. While effective for many, this approach sometimes caused compatibility issues with specific configurations or add-ons. The re-released update offers a more modular approach, providing separate packages for specific components. This allows administrators to apply only the necessary updates, minimizing disruption and reducing the risk of conflicts. Furthermore, improved logging and monitoring features allow for better tracking of the patching process and easier identification of potential problems. This contrasts with previous updates where troubleshooting could be more challenging due to less granular logging.
Step-by-Step Update Installation Guide
Before beginning, always back up your Exchange Server. This crucial step safeguards your data in case of unexpected issues during the update process. Microsoft provides detailed instructions on their support website. Always consult their official documentation for the most accurate and up-to-date guidance.
| Step Number | Action | Expected Result | Troubleshooting |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Download the appropriate update package from the Microsoft Update Catalog. | Successful download of the update package. | Check your internet connection and ensure you have the correct Exchange Server version. Refer to Microsoft’s documentation for the correct package. |
| 2 | Verify the integrity of the downloaded package using a checksum verification tool. | Checksum matches the value provided by Microsoft. | If the checksum does not match, re-download the package. Contact Microsoft support if the issue persists. |
| 3 | Install the update package using the Exchange Management Shell. | Successful installation with no errors reported. | Review the installation log for any error messages. Consult Microsoft’s documentation for troubleshooting specific errors. |
| 4 | Restart the Exchange Server. | Server restarts successfully and all Exchange services are operational. | Check the server logs for any boot errors. If the server fails to start, revert to the previous backup. Contact Microsoft support. |
| 5 | Verify the update installation by checking the Exchange Server version. | The Exchange Server version reflects the newly installed update. | If the version is not updated, re-install the update package. If the issue persists, contact Microsoft support. |
Impact and Affected Systems: Microsoft Re Releases Exchange Server Security Update
The recently re-released Exchange Server security updates address critical vulnerabilities that could have devastating consequences for organizations of all sizes. Understanding the potential impact and the systems affected is crucial for prioritizing immediate action and mitigating risk. Failure to promptly apply these updates leaves your organization exposed to significant threats.
The vulnerabilities patched in this re-release affect a range of Exchange Server versions, highlighting the broad reach of this security concern. The consequences of inaction are far-reaching, impacting not only data integrity but also operational continuity and organizational reputation. The severity of the impact varies depending on the size and structure of the organization, and the specific industries involved face unique challenges.
Affected Exchange Server Versions
This re-release targets specific versions of Microsoft Exchange Server known to be susceptible to the vulnerabilities. Precise version numbers are available on Microsoft’s official security advisories. It’s crucial to verify your Exchange Server version and immediately apply the update if it’s affected. Ignoring the version specifics could lead to a false sense of security and leave your systems vulnerable. Checking your Exchange Server version is the first step towards securing your organization’s data.
Potential Consequences of Not Applying the Update
Failure to install the security updates exposes your organization to a range of severe risks. These include data breaches, leading to the theft of sensitive customer information, intellectual property, or financial records. Malicious actors could gain unauthorized access to your internal systems, potentially disrupting operations, causing financial losses, and damaging your reputation. Furthermore, non-compliance with data protection regulations could result in hefty fines and legal repercussions. The consequences extend beyond simple data loss; they can severely impact your business continuity and long-term viability.
Impact on Organizations of Varying Sizes
The impact of these vulnerabilities varies across organizations of different sizes. Small businesses might face significant disruption and financial strain from a data breach, potentially jeopardizing their survival. Medium-sized businesses could experience substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and legal challenges. Large enterprises, while better equipped to handle the technical aspects, still face considerable costs associated with remediation, recovery, and potential legal action. Regardless of size, the consequences of a successful attack can be catastrophic. For example, a small business could be forced to close due to data loss and associated costs, while a large enterprise might face millions in losses and severe reputational damage.
Industries Particularly Vulnerable
Several industries are particularly vulnerable due to their heavy reliance on Exchange Server and the sensitivity of the data they handle.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations store vast amounts of sensitive patient data, making them a prime target for cyberattacks. A breach could lead to significant legal penalties and irreparable damage to patient trust.
- Finance: Financial institutions handle highly sensitive financial information, making them a lucrative target for attackers seeking financial gain or to disrupt market operations.
- Government: Government agencies handle sensitive citizen data and national security information, making them a high-value target for state-sponsored and other malicious actors.
- Education: Educational institutions store sensitive student and faculty data, making them vulnerable to identity theft and other forms of cybercrime.
Deployment and Mitigation Strategies
Rolling out a critical security update like this Exchange Server patch requires a meticulous, phased approach, especially in large organizations. A rushed deployment can lead to downtime and further vulnerabilities, while a poorly planned rollout can expose your systems to unnecessary risk. Think of it like upgrading a skyscraper – you wouldn’t just replace all the elevators at once, would you?
This section Artikels a practical strategy for deploying the Exchange Server security update, focusing on minimizing disruption and maximizing security. We’ll cover phased rollouts, pre- and post-update checks, and effective log monitoring.
Phased Rollout Plan for Large Enterprises
Implementing the update across a large enterprise demands a phased approach to manage risk and minimize disruption. Consider a four-stage rollout: First, rigorously test the update in a non-production environment mirroring your production setup. Second, deploy to a small pilot group of servers representing different configurations within your infrastructure. Third, roll out to a larger segment, perhaps a department or geographical location. Finally, complete the deployment across the entire organization. This phased approach allows for early identification and resolution of any unforeseen issues before impacting the entire system. Each phase should include thorough monitoring and a rollback plan in case of problems. Think of it as a controlled burn – small, manageable fires are easier to contain than one massive blaze.
Best Practices for Testing in a Non-Production Environment
Before deploying any update to your production servers, it’s crucial to thoroughly test it in a non-production environment. This environment should be as close a replica of your production setup as possible, including similar hardware, software configurations, and network topology. Run comprehensive tests simulating real-world scenarios, including mailbox access, email routing, and other key functionalities. Pay close attention to resource utilization (CPU, memory, disk I/O) during and after the update. Document all test results, noting any anomalies or unexpected behavior. A successful test run in this environment greatly reduces the risk of issues in production. It’s better to find problems in a sandbox than in your live system.
Pre-Update and Post-Update Checklists, Microsoft re releases exchange server security update
Before initiating the update, a thorough checklist is essential. This should include verifying server backups, checking server resource availability, reviewing compatibility with other software, and confirming network connectivity. Post-update validation is equally crucial. Verify service functionality, review system logs for errors or warnings, and monitor resource utilization. Confirm successful email flow and mailbox access. These checks ensure the update has been applied correctly and the system is functioning as expected. Think of this checklist as your pre-flight inspection before taking off.
- Pre-Update Checks: Backup all servers, verify sufficient disk space, review server hardware specs, test network connectivity, review event logs for existing issues.
- Post-Update Checks: Verify service status, review application logs, monitor resource utilization, test email functionality, check for any unusual errors.
Monitoring System Logs for Anomalies
Post-update log monitoring is critical for identifying and addressing any anomalies. Regularly review the Exchange Server logs, the Windows Event Logs, and any other relevant logs. Look for errors, warnings, or unusual activity. Pay close attention to any performance metrics that deviate from the baseline established before the update.
Example Log Entry (Windows Event Log): “Event ID 1001 – Exchange Server detected a critical error during database mounting. Error code: 0x80070002.”
Example Log Entry (Exchange Server Log): “Error: Mailbox database ‘MailboxDatabase01’ failed to mount. Check disk space and permissions.”
Analyzing these logs allows for proactive identification and resolution of potential issues, preventing them from escalating into larger problems. Think of this as your system’s vital signs – monitoring them regularly ensures early detection of any health issues.
Security Best Practices Post-Update
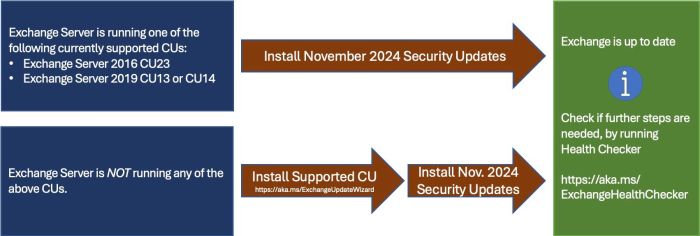
Source: messageware.com
Patching your Exchange Server is a crucial first step, but it’s not the finish line in the race for email security. Think of it like this: you’ve fixed a hole in your fence, but a determined fox might still find a way in. To truly bolster your defenses, you need a multi-layered approach that goes beyond simple updates. This means implementing robust security practices that proactively prevent and detect threats.
Implementing comprehensive security measures post-update significantly reduces the risk of future breaches. Ignoring post-update security best practices leaves your organization vulnerable, potentially leading to data loss, financial penalties, and reputational damage. A proactive strategy ensures your Exchange Server remains secure and resilient against evolving cyber threats.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Scanning
Regular security audits and vulnerability scans are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. These proactive measures identify potential weaknesses in your system before malicious actors can exploit them. Think of them as a comprehensive health check for your Exchange Server. A security audit involves a thorough review of your security policies, procedures, and configurations, while vulnerability scanning uses automated tools to identify known security flaws. Scheduling these audits and scans at least quarterly, or even monthly depending on your risk tolerance, allows for timely remediation of identified vulnerabilities, minimizing your attack surface. For example, a recent audit might reveal outdated software components that need updating, or a misconfiguration that exposes sensitive data. Addressing these issues promptly prevents them from becoming points of entry for attackers.
Multi-Factor Authentication Implementation
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication to access their accounts. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if an attacker obtains a password. Instead of just a password, MFA might require a code from a mobile app, a security key, or biometric verification. Imagine a scenario where an employee’s password is compromised. With MFA enabled, the attacker still needs to bypass the second authentication factor, making it significantly harder to gain access. Implementing MFA across all user accounts is a vital step in protecting your Exchange Server from unauthorized access and data breaches. This significantly reduces the risk of successful phishing attacks, a common vector for gaining access to email accounts.
Employee Education and Training on Email Security
Investing in employee training is crucial for building a strong security culture. Educating your workforce on email security best practices empowers them to identify and avoid phishing attempts, malware, and other threats. This training should cover topics like recognizing phishing emails, understanding the risks of clicking suspicious links, and reporting suspicious activity. Regular training sessions, combined with simulated phishing attacks to test employee awareness, can significantly improve your organization’s resilience against social engineering attacks. For instance, training might include real-world examples of phishing emails, showing employees how to identify subtle cues that indicate a fraudulent message. This hands-on approach helps employees develop the skills needed to protect themselves and the organization from email-borne threats.
Long-Term Security Planning
Ignoring security updates isn’t just a minor inconvenience; it’s a gamble with potentially catastrophic consequences for any organization. In today’s interconnected world, a single vulnerability can expose sensitive data, cripple operations, and inflict significant financial damage. Proactive security planning is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity.
A robust long-term security plan ensures your Exchange Server remains resilient against evolving threats. This involves more than just applying patches; it necessitates a comprehensive strategy encompassing vulnerability identification, prioritization, incident response, and continuous improvement.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Consequences of Neglecting Security Updates
Imagine a mid-sized financial institution neglecting to apply the latest Exchange Server security updates. A sophisticated cyberattack exploiting a known vulnerability breaches their systems, leading to the theft of customer data, including sensitive financial information. The resulting reputational damage, regulatory fines, and legal costs far outweigh the cost of implementing timely updates. This scenario isn’t hypothetical; similar breaches have occurred, resulting in millions of dollars in losses and lasting damage to brand trust. The cost of inaction is significantly higher than the cost of proactive security.
Proactive Vulnerability Identification and Addressing
A proactive approach requires continuous monitoring of security advisories, vulnerability databases (like the National Vulnerability Database – NVD), and utilizing penetration testing and vulnerability scanning tools. Regular security audits, both internal and external, should be conducted to identify potential weaknesses. This proactive approach allows for the identification and remediation of vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors. Automated vulnerability scanning integrated into the IT infrastructure can provide early warnings of emerging threats.
Framework for Managing and Prioritizing Security Updates
A well-defined framework for managing security updates is crucial. This framework should include a clearly defined process for evaluating the severity and urgency of updates, considering factors such as the vulnerability’s impact, the likelihood of exploitation, and the availability of patches. Prioritization should be based on a risk assessment, allocating resources to address the most critical vulnerabilities first. A robust change management process ensures updates are deployed smoothly and with minimal disruption to operations. Regular patching schedules, combined with rigorous testing in a controlled environment before deployment to production, minimize the risk of unintended consequences.
Process for Reporting and Responding to Security Incidents
Effective incident response is paramount. A well-defined process should be in place to quickly identify, contain, and remediate security incidents. This process should involve clear communication channels, escalation procedures, and well-defined roles and responsibilities.
| Incident Type | Detection Method | Response Procedure | Post-Incident Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access Attempt | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) System Alert | Isolate affected systems, investigate the source of the attack, implement countermeasures, and restore system functionality. | Review logs, identify vulnerabilities, and implement preventative measures to avoid future incidents. |
| Malware Infection | Antivirus Software Detection | Quarantine infected systems, remove malware, restore backups, and patch vulnerabilities. | Analyze the malware, identify the attack vector, and improve security defenses. |
| Data Breach | Security Audit, User Report | Contain the breach, investigate the extent of the compromise, notify affected parties, and implement corrective measures. | Conduct a thorough forensic analysis, identify the root cause, and implement preventive measures. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack | Network Monitoring Tools | Mitigate the attack using firewalls and intrusion prevention systems, identify the source, and implement countermeasures. | Analyze attack patterns, strengthen network security, and improve resilience against future attacks. |
Final Wrap-Up

Source: messageware.com
In short, this Microsoft Exchange Server security update is non-negotiable. Ignoring it is akin to leaving your front door unlocked. By understanding the vulnerabilities, implementing the update correctly, and proactively bolstering your overall security posture, you can safeguard your valuable data and maintain business continuity. Don’t just patch; proactively protect your digital assets. The future of your data depends on it.