Elpaco ransomware via RDP: It sounds like a sci-fi thriller, right? But this isn’t fiction. This insidious malware exploits vulnerabilities in your Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to wreak havoc on your systems. We’ll unpack the entire attack chain, from initial infection to data exfiltration, revealing the tactics used by cybercriminals and offering crucial preventative measures. Get ready to learn how to safeguard your digital fortress against this potent threat.
We’ll explore the sneaky ways Elpaco infiltrates systems through weak RDP credentials and unpatched vulnerabilities. We’ll delve into the encryption methods, the ransom demands, and the potential for network-wide damage. Most importantly, we’ll arm you with the knowledge to prevent this nightmare scenario from ever happening to you.
Elpaco Ransomware: Elpaco Ransomware Via Rdp
Elpaco ransomware, like many other strains, leverages Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) vulnerabilities to infiltrate systems. This method offers attackers a relatively straightforward pathway into a network, often bypassing traditional perimeter defenses. Understanding how Elpaco exploits RDP weaknesses is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation.
Elpaco’s success hinges on exploiting vulnerabilities in RDP configurations and user behavior. This allows attackers to gain unauthorized access and deploy the ransomware payload, encrypting sensitive data and demanding a ransom for its release. The attack chain is often surprisingly simple, relying on readily available tools and easily exploitable weaknesses.
RDP Exploitation Methods Used by Elpaco Ransomware
Elpaco ransomware primarily uses brute-force attacks and exploits known vulnerabilities in RDP to gain initial access. Attackers often employ automated tools to test various password combinations against RDP servers, attempting to find weak or default credentials. Additionally, they may scan for and exploit publicly known vulnerabilities in the RDP software itself, using publicly available exploit code or custom-developed tools. Once access is granted, the ransomware is deployed and the encryption process begins.
Elpaco Ransomware Attack Chain via RDP
A typical Elpaco ransomware attack through RDP follows a predictable pattern. First, attackers identify vulnerable RDP servers, often through port scanning or by exploiting publicly available information. They then attempt to authenticate using brute-force techniques or by exploiting known vulnerabilities. Upon successful authentication, they gain shell access to the system. Next, they execute the ransomware payload, which typically involves disabling security software and encrypting files. Finally, a ransom note is displayed, demanding payment in cryptocurrency for the decryption key.
Leveraging Weak or Default RDP Credentials
The use of weak or default passwords is a significant factor in RDP-based ransomware attacks. Many organizations fail to enforce strong password policies, leading to easily guessable credentials. Similarly, the use of default RDP accounts with easily discovered passwords provides attackers with an immediate entry point. Attackers frequently use password cracking tools and lists of common passwords to gain access to these accounts. The failure to change default credentials is a common vulnerability exploited by attackers, highlighting the importance of strong password management practices.
Malicious Code and Techniques in RDP-Based Elpaco Infections
The specific malicious code used by Elpaco may vary, but common techniques include the use of PowerShell scripts to download and execute the ransomware payload, disabling security software through registry manipulation, and using encryption algorithms to encrypt files. Attackers often employ techniques to evade detection by antivirus software, such as using obfuscation or packing techniques to hide the malicious code.
| Attack Vector | Exploitation Method | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| RDP Brute-forcing | Automated tools testing password combinations | Unauthorized access, ransomware deployment | Strong password policies, multi-factor authentication |
| RDP Vulnerability Exploit | Exploiting known vulnerabilities in RDP software | System compromise, data encryption | Regular software updates, patching vulnerabilities |
| Default RDP Credentials | Using default or easily guessable credentials | Immediate system access, ransomware deployment | Changing default credentials, enforcing strong password policies |
| Phishing/Social Engineering | Tricking users into providing RDP credentials | Unauthorized access, ransomware deployment | Security awareness training for employees |
Elpaco Ransomware: Elpaco Ransomware Via Rdp
Source: esecurityplanet.com
Elpaco ransomware, delivered often via compromised RDP connections, represents a significant threat to individual users and businesses alike. Understanding its payload and encryption mechanisms is crucial for effective mitigation and recovery. This section details the technical aspects of the ransomware’s operation, providing insights into its targets and demands.
Encryption Algorithm and Process
While the precise algorithm employed by Elpaco ransomware isn’t publicly available, analysis suggests the use of a robust, asymmetric encryption method. This likely involves a combination of encryption keys – a public key for encrypting files and a private key held by the attackers for decryption. The encryption process itself probably begins with identifying target files based on their extensions and types. The ransomware then iterates through these files, encrypting each one individually using the public key. This process generates a unique ciphertext for each file, rendering it inaccessible without the corresponding private key. The speed of encryption depends on several factors including the file size, the processing power of the infected machine, and the encryption algorithm’s efficiency. Larger files naturally take longer to encrypt.
Targeted File Types and Extensions
Elpaco ransomware typically targets a wide range of file types crucial for both personal and professional use. Commonly affected extensions include, but are not limited to, .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .pdf, .jpg, .jpeg, .png, .zip, and various database files. The ransomware prioritizes files with high value to the victim, aiming to maximize the impact of the attack and the likelihood of a ransom payment. The specific files targeted can vary depending on the ransomware variant and the configuration used by the attackers. For instance, some versions might specifically target financial records or project files, depending on the attacker’s intelligence on the victim’s system.
Ransom Note Content and Payment Methods
The ransom note delivered by Elpaco ransomware typically contains instructions for payment, often including a unique identifier linking the victim to their encrypted files. The note usually demands a ransom payment in cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Monero, to ensure anonymity for the attackers. The amount demanded varies, often depending on the perceived value of the compromised data and the victim’s perceived ability to pay. The note often includes a timeframe for payment, implying a potential increase in the ransom amount or permanent data loss if the deadline is missed. The attackers often provide a contact method, usually through an encrypted email address or a dark web forum, for victims to negotiate or obtain further instructions. They might also offer a “free decryption” of a limited number of files as a demonstration of their capabilities and to encourage payment.
Elpaco Ransomware: Elpaco Ransomware Via Rdp

Source: rdp.monster
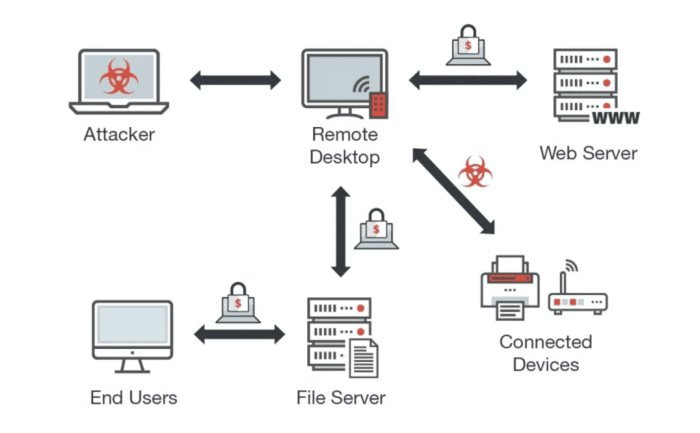
Elpaco ransomware, after gaining initial access via RDP, doesn’t simply encrypt your files and call it a day. It’s a sophisticated threat that actively seeks to expand its reach within your network, maximizing the damage and the ransom demand. Understanding its lateral movement techniques is crucial for effective prevention and response.
Elpaco’s network propagation relies on a combination of established and emerging techniques, making it a particularly dangerous threat. Its ability to evade detection and disable security software further compounds the problem, often leaving organizations scrambling to contain the damage.
Lateral Movement Techniques
Once inside, Elpaco uses several methods to spread. It leverages readily available tools and exploits known vulnerabilities to move between systems. Common techniques include exploiting weak passwords on other machines accessible via network shares, using compromised credentials to access other RDP endpoints, and leveraging PowerShell scripts for lateral movement and command execution. This allows the ransomware to infect multiple servers and workstations within a network rapidly. For instance, if a user has the same password across multiple systems, Elpaco can easily move from one compromised machine to the next. The speed and efficiency of this process highlight the critical need for robust password management and network segmentation.
Disabling Security Software and Evasion Techniques, Elpaco ransomware via rdp
Elpaco employs various techniques to evade detection and disable security software. This can include terminating security processes, disabling Windows Defender or other antivirus programs, and modifying registry settings to prevent automatic updates and scans. Furthermore, it might utilize techniques like process injection or code obfuscation to hide its malicious activities from endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions. For example, it might inject its code into legitimate processes to mask its presence, making it harder to identify and remove. This requires a multi-layered security approach, including strong endpoint protection, network security monitoring, and regular security audits.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Identifying Elpaco’s presence often relies on recognizing specific IOCs. These could include unusual network traffic patterns, such as a sudden surge in outbound connections to command-and-control (C&C) servers. The presence of suspicious processes or files associated with Elpaco’s known hashes or signatures is another key indicator. Unusual registry modifications, especially those related to security software or scheduled tasks, should also raise red flags. Finally, the appearance of ransom notes with specific Elpaco branding or encryption patterns helps confirm the attack. Regular security monitoring and log analysis are crucial for timely detection of these IOCs.
Network Diagram Illustrating Lateral Movement
Imagine a network with three machines: A (the initially compromised machine), B (a file server), and C (a database server).
Imagine a simple diagram:
A (RDP compromised) —(Network Share Access)–> B (File Server) —(Network Share Access)–> C (Database Server)
In this scenario, Elpaco initially compromises machine A via RDP. It then uses credentials obtained from A to access a network share, granting it access to machine B (the file server). From there, it might use similar methods to access machine C (the database server). This shows how quickly ransomware can spread through a network if security measures are insufficient. Each successful hop represents a potential encryption event, significantly increasing the impact of the attack. Network segmentation and access control lists (ACLs) are vital to prevent this type of lateral movement.
Elpaco Ransomware: Elpaco Ransomware Via Rdp
Elpaco ransomware, like many of its malicious brethren, doesn’t just encrypt your files and leave you high and dry. It often employs a double extortion tactic, meaning it not only encrypts your data but also steals it before doing so. This stolen data becomes leverage, increasing the pressure on victims to pay the ransom. Understanding how Elpaco exfiltrates this data is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation.
The process of data exfiltration by Elpaco ransomware involves several steps, from identifying valuable targets to securely transferring the stolen information to the attacker’s servers. This is a carefully orchestrated operation, often relying on techniques designed to remain undetected for as long as possible.
Data Exfiltration Techniques
Elpaco likely uses a combination of techniques to exfiltrate data. These techniques are designed to be stealthy and efficient, often leveraging readily available tools and infrastructure. The ransomware might initially scan the compromised system to identify high-value targets such as databases, financial records, intellectual property, and customer information. Once these targets are identified, the ransomware will initiate the data transfer process, often employing techniques that minimize the chances of detection. This might involve using encrypted connections, obfuscated commands, and segmented data transfers to evade security systems. The speed of data exfiltration depends on factors like network bandwidth, the volume of data targeted, and the sophistication of the attacker’s infrastructure.
Targeted Data Types
Elpaco, like other ransomware operations, focuses on data with high value to the victim. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Databases: Containing sensitive customer information, financial records, or proprietary business data.
- Documents: Including financial statements, contracts, research papers, and intellectual property.
- Images and Videos: Potentially containing sensitive information or proprietary designs.
- Backup Files: These are often specifically targeted to cripple recovery efforts.
- Email Archives: Containing sensitive communications and potentially revealing valuable business intelligence.
Potential Data Exfiltration Channels
The attackers behind Elpaco ransomware likely utilize a variety of channels to exfiltrate stolen data. The choice of channel often depends on factors like the size of the data, the security measures in place, and the attacker’s resources.
Understanding these channels is key to implementing effective security measures.
- Cloud Storage Services: Attackers might upload stolen data to compromised or newly created cloud storage accounts, leveraging the ease of access and scalability these services offer.
- File Transfer Protocols (FTP/SFTP): These established protocols provide a reliable means of transferring files to remote servers, often using encrypted connections to mask the transfer.
- Email: While less common for large datasets, smaller files might be exfiltrated via email attachments or through the use of compromised email accounts.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Networks: These decentralized networks offer a degree of anonymity, making them an attractive option for exfiltrating data more discreetly.
- Dark Web Forums and Marketplaces: Stolen data can be sold or traded on these underground platforms, providing a readily available market for the stolen information.
Elpaco Ransomware: Elpaco Ransomware Via Rdp
Elpaco ransomware, like other variants, exploits vulnerabilities to encrypt your valuable data, demanding a ransom for its release. Understanding how it operates is crucial, but equally important is knowing how to prevent infection and mitigate its impact. Proactive security measures are far more effective and cost-efficient than reactive cleanup. This section details practical steps to fortify your systems against Elpaco and similar threats.
Securing RDP Servers Against Elpaco Ransomware
Robust security for RDP servers requires a multi-layered approach. Leaving RDP open to the internet without proper authentication is an open invitation to attackers. The following best practices significantly reduce the risk of a successful Elpaco ransomware attack.
- Disable RDP on the internet: Directly expose RDP only to trusted internal networks. Use a VPN for remote access.
- Restrict Access by IP Address: Configure RDP to only accept connections from specific IP addresses or subnets known to be legitimate.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct frequent security audits to identify and address any misconfigurations or vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate your RDP servers from other critical systems. If compromised, the damage is contained.
- Strong Firewall Rules: Implement strict firewall rules that only allow necessary traffic to and from the RDP server.
Configuring Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Weak passwords are the easiest entry point for attackers. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, making it exponentially harder for malicious actors to gain access.
Strong passwords should be at least 12 characters long, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid easily guessable information like names, dates, or common words. Password managers can help you generate and securely store complex passwords.
MFA requires multiple forms of authentication. Common methods include one-time codes generated by authenticator apps (like Google Authenticator or Authy), security keys (like YubiKeys), or biometric authentication. Enabling MFA for RDP access is a critical step in enhancing security.
Regular Patching and Software Updates
Software vulnerabilities are constantly being discovered and exploited by cybercriminals. Regular patching and updates are essential to ensure that your systems are protected against the latest threats. Elpaco, and other ransomware, often leverage known vulnerabilities to gain initial access.
Implement a robust patching schedule that includes all operating systems, applications, and firmware. Automate the update process whenever possible to minimize the risk of neglecting updates. Keep track of updates and ensure that all systems are up-to-date.
Implementing Network Segmentation
Network segmentation divides your network into smaller, isolated segments. This limits the impact of a security breach. If one segment is compromised, the ransomware cannot easily spread to other critical parts of your network.
For example, you could separate your RDP servers from your database servers and file servers. If an attacker gains access to the RDP server, they are contained within that segment and cannot directly access sensitive data on other servers.
Elpaco Ransomware: Elpaco Ransomware Via Rdp
Elpaco ransomware, like many other ransomware variants, presents a significant cybersecurity threat. Understanding its mechanics and the forensic approach to investigating an attack is crucial for effective remediation and prevention. This section details key aspects of a forensic analysis of an Elpaco ransomware infection, focusing on data recovery possibilities and attack reconstruction.
Forensic Analysis Key Areas
A forensic investigation into an Elpaco ransomware attack should prioritize several key areas. These include identifying the initial infection vector (e.g., phishing email, compromised RDP connection, software vulnerability), analyzing the ransomware’s encryption algorithm and key generation methods, and recovering encrypted files if possible. Furthermore, examining system logs and network traffic for indicators of compromise (IOCs) is vital for understanding the attacker’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). Finally, the investigation should aim to identify any persistence mechanisms used by the ransomware to ensure its survival across system restarts.
Encrypted File Recovery
Recovering encrypted files after an Elpaco ransomware attack depends heavily on several factors, including the ransomware’s encryption strength, the availability of decryption keys, and the presence of unencrypted file backups. In some cases, security researchers might release decryption tools if a weakness in the ransomware’s encryption algorithm is discovered. However, this is not always guaranteed. The most reliable method of recovering encrypted files is through the use of regularly backed-up data. If backups exist, restoring the system from a pre-infection backup is the most effective recovery strategy. Without backups, recovery is far less certain and may require specialized data recovery tools, which are not always successful.
Network Log and System Event Analysis
Analyzing network logs and system events is crucial for reconstructing the attack timeline. Network logs can reveal the source of the infection, the communication channels used by the ransomware, and the exfiltration of stolen data. System logs, on the other hand, can show the ransomware’s actions on the affected system, including file creation, modification, and deletion events. By correlating network and system logs, investigators can build a detailed picture of the attack, including the initial access point, the lateral movement of the attacker (if any), and the encryption process. For example, analyzing Windows Event Logs for suspicious process creations, network connections, and file system activity around the time of the attack is critical.
Forensic Artifact Checklist
A thorough forensic investigation requires the collection of various artifacts. These artifacts can provide critical evidence for understanding the attack and potentially recovering data. The following checklist highlights some key artifacts to collect:
- Memory dump: A snapshot of the system’s RAM at the time of the investigation, which may contain remnants of the ransomware’s processes and encryption keys.
- Registry keys: Examination of the Windows Registry for any malicious registry entries created by the ransomware.
- System logs: Windows Event Logs, application logs, and other system logs that record system activity.
- Network logs: Logs from routers, firewalls, and other network devices that record network traffic.
- Encrypted files: Samples of the encrypted files, including their metadata and file extensions.
- Ransom note: The text file left behind by the ransomware containing instructions for payment.
- Prefetch files: Files that contain information about recently executed programs, which may include the ransomware executable.
- Shadow copies: Volume Shadow Copies (VSS) may contain previous versions of files that were encrypted.
Closing Notes
Source: buy-rdp.com
Elpaco ransomware via RDP is a serious threat, but understanding its attack vectors and mitigation strategies is your first line of defense. By strengthening your RDP security, implementing robust patching practices, and staying vigilant, you can significantly reduce your risk. Remember, proactive security is cheaper than reactive recovery. Don’t wait until it’s too late – secure your systems today.





