Windows zero days firefox romcom group – Windows Zero Days, Firefox, Rom-Coms & Groupthink: Sounds like the start of a wild movie plot, right? But the reality of zero-day vulnerabilities in Windows and Firefox is far from fictional. This isn’t just about tech geeks; it’s about how a single software weakness can unravel even the most carefully planned systems – and how the way we work together can either save the day or make things a whole lot worse. We’re diving into the world of zero-day exploits, exploring the security features (or lack thereof) in popular software, and even throwing in a dash of rom-com flair to make learning about cybersecurity a little less…dry.
We’ll unpack the technical aspects of zero-day vulnerabilities, examining how they’re exploited and the crucial role of software updates in preventing disaster. We’ll also explore the human element, analyzing how group dynamics and communication styles impact a team’s ability to respond to a crisis. Think of it as a crash course in cybersecurity with a side of rom-com escapism – because learning about potential digital doom doesn’t have to be a total bummer.
Windows Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Source: slideplayer.com
The discovery of a zero-day vulnerability in a Windows operating system is a serious event, potentially causing significant disruption and damage. These flaws, unknown to the software developer, offer attackers a direct route into a system before a patch is available, making them particularly dangerous. Understanding the impact, exploitation methods, and mitigation strategies is crucial for both individuals and organizations.
Potential Impact of Windows Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
A successful exploit of a Windows zero-day vulnerability can have devastating consequences. Attackers can gain complete control of a compromised system, potentially stealing sensitive data, installing malware, launching further attacks against other systems (botnets), or disrupting services. The impact can range from individual data breaches to large-scale corporate espionage or even critical infrastructure failures. The financial and reputational damage can be immense, depending on the sensitivity of the compromised data and the scale of the attack. The lack of a readily available patch makes remediation complex and time-consuming, exacerbating the problem.
Common Exploitation Methods
Attackers typically leverage various methods to exploit Windows zero-day vulnerabilities. These methods often involve sophisticated techniques like social engineering (tricking users into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments), exploiting vulnerabilities in web browsers or other applications, or using drive-by downloads to infect systems without user interaction. Once access is gained, attackers may employ techniques like privilege escalation to gain administrator-level control, allowing them to install persistent malware and maintain access over time. The complexity of the attack vectors varies depending on the specific vulnerability and the attacker’s skill level. Zero-day exploits are often highly targeted and customized for specific systems or organizations.
Role of Software Updates in Mitigating Zero-Day Risks
Regular software updates are the most effective defense against zero-day vulnerabilities. Microsoft regularly releases security patches that address known vulnerabilities, including many zero-days that have been privately disclosed or discovered independently. Keeping the Windows operating system, applications, and antivirus software up-to-date significantly reduces the risk of successful exploitation. This proactive approach minimizes the window of opportunity for attackers to leverage these vulnerabilities before they are patched. Enabling automatic updates is highly recommended to ensure timely patching and minimal disruption.
Examples of Real-World Scenarios
Several high-profile incidents have demonstrated the real-world impact of Windows zero-day exploits. The following table summarizes some notable examples:
| Vulnerability Name | Date Discovered (Approximate) | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stuxnet | 2010 | Disrupted Iranian nuclear program through sophisticated malware targeting industrial control systems. | Improved security practices, network segmentation, and enhanced patching procedures. |
| Equation Group exploits | 2015 (Ongoing) | Targeted governments and organizations, stealing sensitive data and maintaining persistent access to systems. | Advanced threat detection and response systems, improved network security, and robust patching practices. |
| Various browser exploits | Ongoing | Used in targeted attacks to deliver malware via compromised websites or malicious advertisements. | Using up-to-date browsers with enabled automatic updates, and avoiding suspicious websites. |
| EternalBlue (MS17-010) | 2017 | Exploited a vulnerability in the SMB protocol, leading to the WannaCry ransomware outbreak. | Applying the security patch released by Microsoft (MS17-010). |
Firefox Security and Zero-Days
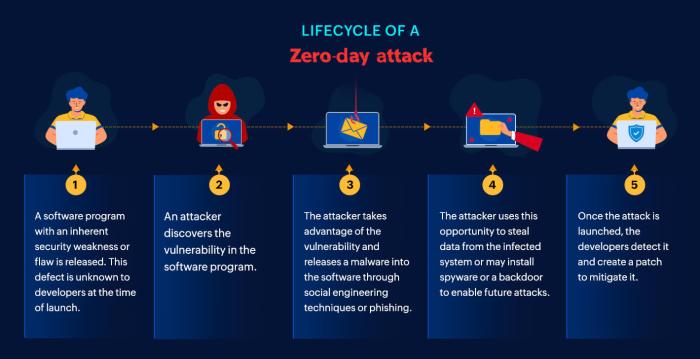
Source: manageengine.com
Firefox, despite its reputation for being a user-friendly browser, boasts a robust security architecture designed to proactively defend against even the most sophisticated zero-day exploits. This isn’t just about patching vulnerabilities after they’re found; it’s about a multi-layered approach that aims to minimize the impact of unknown threats.
Firefox’s security model relies on a combination of proactive and reactive measures. Proactive measures include features like sandboxing, which isolates potentially malicious processes to limit their damage, and advanced memory protection techniques that make it harder for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. Reactive measures, meanwhile, involve a rapid response system for patching newly discovered vulnerabilities, along with a strong community of security researchers who constantly scan for and report potential weaknesses.
Firefox’s Security Features
Firefox employs several key security features to mitigate zero-day attacks. These include, but aren’t limited to, sandboxing technology that isolates web content from the operating system, preventing malicious code from accessing sensitive files or system resources. Furthermore, memory protection mechanisms such as Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) and Data Execution Prevention (DEP) make it significantly harder for attackers to inject and execute malicious code. Regular automatic updates ensure that users always have the latest security patches. Finally, the browser utilizes a sophisticated process of verifying code signatures and certificates to authenticate websites and prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Comparison with Other Browsers
While all major browsers incorporate security measures, their approaches and effectiveness can vary. For example, Chrome’s focus on speed and ease of use sometimes prioritizes performance over granular security controls, while Safari, due to its integration with Apple’s ecosystem, leverages Apple’s own security infrastructure. Firefox, however, aims to strike a balance between user experience and comprehensive security, often emphasizing transparency and user control over security settings. A key difference lies in Firefox’s open-source nature, which allows for community scrutiny and independent security audits, fostering a more robust and resilient security ecosystem.
Firefox’s Vulnerability Response Process
When a zero-day vulnerability is discovered in Firefox, a coordinated response is initiated. This process involves internal security teams validating the vulnerability, developing a patch, and then rapidly deploying that patch to all users via automatic updates. The speed and efficiency of this process are crucial in minimizing the potential impact of the vulnerability. Furthermore, Firefox actively engages with the security research community, offering bug bounty programs and encouraging responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities to ensure proactive identification and remediation.
Hypothetical Zero-Day Exploit Scenario
Imagine a sophisticated zero-day exploit targeting a vulnerability in Firefox’s JavaScript engine. This exploit could allow an attacker to inject malicious code into a seemingly benign webpage. Upon visiting the compromised website, a user’s browser would unknowingly execute the malicious code. The attacker could then gain access to the user’s sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, or personal files. This could lead to identity theft, financial loss, and serious privacy violations. The impact would be exacerbated if the exploit allowed for remote code execution, enabling the attacker to take complete control of the user’s computer. A real-world example, though not directly related to Firefox, is the widespread use of exploits targeting vulnerabilities in Adobe Flash Player, which demonstrated the severe consequences of such zero-day vulnerabilities. The rapid spread of malware and the resulting damage highlighted the urgent need for quick patching and responsible disclosure.
The Role of Software Updates
Keeping your software updated is like regularly servicing your car – it prevents small problems from becoming major breakdowns. Ignoring updates leaves your digital life vulnerable to cyber threats, crashes, and frustrating performance issues. Regular updates patch security holes, improve performance, and add new features, ensuring a smoother and safer computing experience.
Regular updates are the unsung heroes of a secure digital life. They’re not glamorous, but they’re essential for protecting your data and maintaining a stable system. Failing to update exposes you to a world of potential problems, from annoying glitches to devastating data breaches. Let’s dive into the specifics of keeping your Windows and Firefox software current.
Updating Windows and Firefox
Updating Windows and Firefox is a straightforward process, though the exact steps might vary slightly depending on your operating system version. For Windows, typically, you’ll find the update settings within the Settings app. Navigate to “Update & Security,” then “Windows Update.” Click “Check for updates” and follow the on-screen instructions to download and install any available updates. This might involve restarting your computer. For Firefox, the process is equally simple. Click the three horizontal lines (the menu button) in the top right corner of the browser window. Select “Help” and then “About Firefox.” Firefox will automatically check for updates and download them. A restart might be required to complete the update.
The Importance of Enabling Automatic Updates
Enabling automatic updates for both Windows and Firefox is crucial for maintaining a secure and up-to-date system. Automatic updates ensure that you always have the latest security patches and performance improvements installed without needing to manually check for them. This proactive approach minimizes the window of vulnerability and reduces the risk of falling victim to malware or exploits. Imagine it like this: automatic updates are your system’s personal bodyguard, constantly scanning for and neutralizing threats before they can even reach you.
Risks Associated with Delaying Software Updates
Delaying software updates exposes your system to a range of potential risks. Outdated software is significantly more vulnerable to malware, viruses, and other cyber threats. Hackers constantly seek vulnerabilities in older software versions, exploiting them to gain unauthorized access to your system and data. Delayed updates can also lead to performance issues, compatibility problems, and even system crashes. For example, a delay in updating your browser could leave you susceptible to phishing attacks, potentially leading to identity theft or financial loss. Consider the case of the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017, which exploited a known vulnerability in older versions of Windows. Millions of computers were affected, causing significant disruption and financial damage.
Best Practices for Ensuring Software is Up-to-Date and Secure
Maintaining up-to-date software is a multi-faceted process that requires proactive engagement. Here are some best practices to ensure your systems remain secure:
- Enable automatic updates for all software, including operating systems, browsers, and applications.
- Regularly check for updates manually, even if automatic updates are enabled.
- Install updates as soon as they are available, prioritizing security patches.
- Use a reputable antivirus and anti-malware program and keep it updated.
- Be cautious when downloading software from unknown sources; stick to official websites.
- Keep your passwords strong and unique, and practice good password management.
- Regularly back up your important data to prevent data loss in case of a system failure.
Rom-Com Themes and Cybersecurity
Let’s face it, cybersecurity isn’t exactly known for its romantic appeal. But what if we injected a little bit of rom-com magic into the world of zero-day exploits and phishing scams? Suddenly, the stakes are higher than just a stolen password – they’re the potential demise of a budding relationship! We’ll explore how the charming chaos of rom-coms can actually be a surprisingly effective way to teach us about the very real dangers lurking online.
A rom-com scenario involving a zero-day vulnerability could unfold like this: Our heroine, a brilliant but slightly clumsy cybersecurity analyst named Chloe, discovers a critical zero-day vulnerability in a popular dating app. Meanwhile, our charmingly clueless hero, Liam, a software developer with a penchant for cheesy pick-up lines, is unknowingly using the very app Chloe is trying to save. The vulnerability allows malicious actors to access user data, including private photos and location information – potentially ruining Liam’s chances with Chloe before they even have a first date!
Character Reactions to a Cybersecurity Incident, Windows zero days firefox romcom group
Chloe’s initial reaction is a mix of professional concern and personal panic. She’s racing against the clock to patch the vulnerability before it’s exploited on a massive scale, all while trying to subtly warn Liam (without revealing her professional obsession with his dating app habits). Liam, bless his heart, initially dismisses Chloe’s warnings as overly cautious, only to become increasingly alarmed as strange things start happening: His profile mysteriously gets flooded with inappropriate messages, his location is shared publicly, and he starts receiving phishing emails. The escalating situation forces Liam to finally understand the gravity of the situation and appreciate Chloe’s expertise. This shared crisis brings them closer together, highlighting the importance of cybersecurity not just for personal privacy, but for the success of their relationship.
Using Rom-Com Tropes to Educate About Cybersecurity Risks
Rom-coms thrive on misunderstandings, near-misses, and ultimately, happy resolutions. These very tropes can be used to illustrate the consequences of poor cybersecurity practices. For example, the “meet-cute” could involve a shared experience of a data breach, showcasing the widespread impact of vulnerabilities. The classic “will-they-won’t-they” tension could be mirrored by the constant threat of a successful exploit. And the final, heartwarming resolution could symbolize the successful patching of a vulnerability and the triumph of good over evil (or at least, over malicious hackers). By embedding these cybersecurity lessons within a familiar and engaging narrative, we can make complex technical issues relatable and understandable to a broader audience.
A Rom-Com Scene: Discovering and Reporting a Vulnerability
[SCENE START]
INT. CHLOE’S APARTMENT – NIGHT
Chloe, hunched over her laptop, stares intently at a line of code. Empty coffee cups surround her. She’s been working late, analyzing the dating app’s security. A triumphant grin spreads across her face.
CHLOE
(whispering)
Bingo!
She types furiously, documenting her findings. She then carefully crafts a detailed report, outlining the vulnerability and its potential impact. She attaches screenshots and logs as evidence. She sends the report to the app’s security team, a mix of relief and adrenaline coursing through her.
CHLOE
(to herself)
Okay, Chloe. Mission accomplished. Now, maybe a little sleep before Liam’s next disastrous date.
[SCENE END]
Group Dynamics and Cybersecurity Awareness: Windows Zero Days Firefox Romcom Group
Imagine a bustling office, phones ringing, emails flooding in – then BAM! A zero-day vulnerability hits. How your team handles this crisis depends heavily on their group dynamics. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for building a resilient cybersecurity posture. Effective teamwork, clear communication, and recognizing individual strengths and weaknesses are key to mitigating the damage and swiftly recovering from such an attack.
The influence of group dynamics on an organization’s response to a zero-day vulnerability is significant. A well-coordinated team with established communication channels and clear roles will likely respond more effectively than a group plagued by internal conflicts or poor communication. The speed and efficiency of a response directly impact the extent of the damage caused by the vulnerability. A cohesive team can quickly identify the threat, contain the damage, and implement a solution, minimizing disruption and financial losses. Conversely, a dysfunctional team might experience delays, confusion, and even exacerbate the problem through conflicting actions or missed deadlines.
Effective Communication and Collaboration in Cybersecurity Threat Response
Effective communication and collaboration are paramount during a cybersecurity crisis. This involves a multi-faceted approach. First, a clearly defined incident response plan should exist, outlining roles, responsibilities, and escalation procedures. Regular drills and simulations allow teams to practice their response, improving coordination and identifying potential bottlenecks. Second, real-time communication channels, such as dedicated chat platforms or conference calls, enable rapid information sharing and decision-making. Third, clear and concise reporting ensures that everyone is informed about the situation’s progress and their individual tasks. For instance, a daily update email to all relevant stakeholders with a summary of the incident, actions taken, and next steps can significantly improve coordination. Finally, post-incident reviews allow for critical analysis of the response, identifying areas for improvement in future incidents. This continuous improvement cycle is vital for building a robust and resilient security posture.
Potential Communication Barriers Hindering Zero-Day Incident Response
Several communication barriers can hinder a group’s response to a zero-day incident. Siloed departments, where different teams lack visibility into each other’s work, can lead to duplicated efforts, missed deadlines, and conflicting actions. Technical jargon, used excessively without explanation, can create confusion and impede understanding among team members with varying levels of technical expertise. Lack of trust among team members can prevent open communication and the sharing of crucial information. Fear of blame or retribution can also discourage individuals from reporting potential problems or admitting mistakes, delaying the response and potentially worsening the situation. For example, if a junior technician discovers a vulnerability but fears reprimand for not identifying it sooner, they might delay reporting, allowing the vulnerability to be exploited further. Finally, differing communication styles and preferences can hinder effective information exchange. Some individuals might prefer written communication while others prefer verbal updates, leading to misunderstandings and delays if not carefully managed.
Different Personality Types and Cybersecurity Crisis Reactions
Different personality types react differently to a cybersecurity crisis. For instance, individuals with a high need for control might become overly assertive, potentially hindering collaborative efforts. Others might freeze under pressure, delaying necessary actions. Those with a strong risk-averse personality might overreact, implementing unnecessary security measures that could disrupt operations. Conversely, individuals with a more adaptable and resilient personality might handle the crisis more calmly and effectively, finding creative solutions under pressure. Understanding these different reactions is key to building a team that can handle the stress and pressure of a cybersecurity incident effectively. For example, pairing a detail-oriented individual with a more broadly strategic thinker can create a balanced response team, allowing for both meticulous investigation and high-level decision-making. Recognizing these personality traits and assigning roles accordingly can optimize the team’s response to a crisis.
Visual Representation of a Zero-Day Exploit
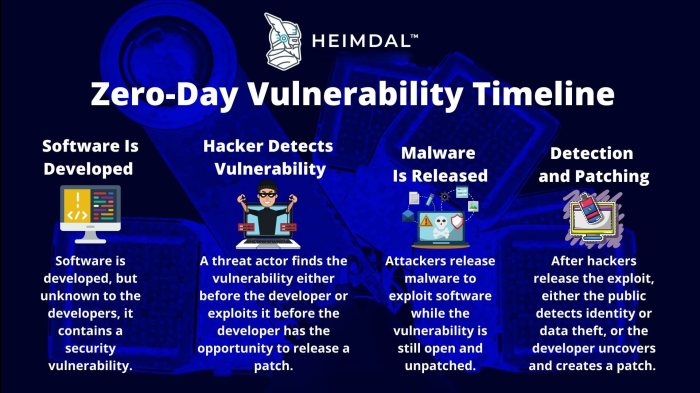
Source: heimdalsecurity.com
Imagine a bustling city street, representing your computer system. Windows is the main thoroughfare, bustling with activity, and Firefox is a busy side street, handling web traffic. A zero-day exploit is like a cleverly disguised getaway car, unnoticed by the city’s security (your antivirus and firewall).
This visual representation would depict the attack’s progression. Initially, the scene shows normal activity – people (data packets) moving smoothly along the streets. Then, the getaway car (the exploit) enters, seemingly innocuous. It blends in with the regular traffic, perhaps disguised as a delivery truck (a seemingly harmless file or link). The car (exploit) approaches a specific building (a vulnerable application within Firefox or a Windows service). It smoothly bypasses the security checkpoints (antivirus, firewall) because they haven’t been updated to recognize this particular threat. Once inside the building, the car (exploit) swiftly gains access to valuable items (sensitive data) and quietly escapes. The visual would show a subtle change in the scene – perhaps a slight flicker of light or a subtle change in the building’s appearance – representing the successful compromise. The final scene would depict the getaway car speeding away, leaving behind a compromised system, oblivious to the theft that just occurred.
Visual Representation of a Successful Mitigation Strategy
In contrast to the chaotic scene of the exploit, the successful mitigation strategy visual would showcase a well-organized and fortified city. The main thoroughfares (Windows and Firefox) are now equipped with enhanced security systems – think robust walls (updated operating system and browser), sophisticated surveillance cameras (real-time threat detection), and vigilant security guards (firewall and antivirus with updated signatures). The city’s security has learned from past attacks and has implemented preventative measures. The visual could show the “getaway car” (the exploit) attempting to enter the city, but it’s immediately detected by the surveillance cameras and stopped by the security guards before it can reach its target. The car is then safely removed from the city, and the system remains secure. The visual would emphasize the proactive nature of the mitigation strategy, highlighting the importance of regular software updates, strong security protocols, and robust security software. The overall feel would be one of calm and control, in stark contrast to the previous visual’s tension and chaos. This contrasts sharply with the previous chaotic scene, showcasing the peace of mind provided by a well-defended system.
Final Summary
So, there you have it – a whirlwind tour through the surprisingly intertwined worlds of Windows zero-days, Firefox security, the surprisingly relatable drama of rom-coms, and the often-chaotic dynamics of group responses to cyber threats. While the technical details might seem daunting, the core message is simple: staying updated, communicating effectively, and understanding the risks are crucial to navigating the digital landscape safely. Think of it as your personal cybersecurity rom-com, where the happy ending depends entirely on your proactive approach. Now go forth and update your software!





