Zoom app vulnerability: It’s a phrase that’s become increasingly familiar, whispering anxieties about privacy and security in our hyper-connected world. From seemingly innocuous glitches to full-blown security breaches, the potential impact on individuals and organizations is significant. This isn’t just about awkward background noise anymore; we’re talking about sensitive data, compromised accounts, and the potential for widespread disruption. Let’s unpack the complexities of Zoom’s security landscape.
This exploration delves into the various types of Zoom vulnerabilities, ranging from easily exploitable flaws to more sophisticated attacks. We’ll dissect the methods used by malicious actors to infiltrate systems, examining everything from social engineering tactics to technical exploits. We’ll also provide practical strategies for mitigation, emphasizing the importance of proactive security measures and staying ahead of emerging threats. Because let’s be honest, in the digital age, being informed is your best defense.
Zoom App Vulnerabilities
Zoom, despite its popularity, hasn’t been immune to security hiccups. From privacy concerns to outright security flaws, the platform has faced its share of vulnerabilities, impacting both individual users and large organizations. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring secure communication.
Zoom App Vulnerability Categories and Severity
Zoom vulnerabilities fall into several categories, each with varying degrees of severity and impact. These range from minor annoyances to critical security breaches that could expose sensitive information or disrupt services. Understanding these categories helps users and organizations prioritize security measures.
| Vulnerability Type | Severity | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Flaws | Critical | Exploitable weaknesses in the application’s code that allow unauthorized access, data manipulation, or denial-of-service attacks. Examples include buffer overflows or insecure authentication mechanisms. | Data breaches, unauthorized access to meetings, system compromise, financial loss, reputational damage. |
| Privacy Breaches | High | Vulnerabilities that expose user data, such as meeting content, participant information, or chat logs, without consent. This can include weaknesses in data encryption or insufficient access controls. | Loss of confidential information, identity theft, legal repercussions, erosion of user trust. For example, the exposure of meeting links could lead to uninvited participants joining sensitive discussions. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks | High | Attacks that overwhelm Zoom servers, rendering the service unavailable to legitimate users. These can be targeted or widespread, impacting both individual users and entire organizations. | Disruption of communication, loss of productivity, financial losses due to downtime, damage to reputation. A large-scale DoS attack could cripple an organization’s ability to conduct meetings or webinars. |
| Session Hijacking | Medium | An attacker gains unauthorized access to a user’s Zoom session, potentially viewing or manipulating meeting content. This could occur through exploiting vulnerabilities in the authentication process or by intercepting session cookies. | Exposure of sensitive information shared during the meeting, unauthorized control over meeting settings. For instance, an attacker might share malicious content or disrupt the meeting flow. |
| Insufficient Access Controls | Medium | Weaknesses in access control mechanisms allow unauthorized users to access meetings or features they shouldn’t have access to. This can include weak password policies or a lack of robust user authentication. | Data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, disruption of meetings. For example, a poorly configured meeting could allow anyone to join and view confidential information. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Low | Vulnerabilities that allow attackers to inject malicious scripts into Zoom’s web interface, potentially stealing user cookies or redirecting users to phishing sites. | Compromised user accounts, malware infections, data theft. While potentially less severe than other vulnerabilities, XSS attacks can still have significant consequences. |
Examples of Real-World Zoom Vulnerabilities and Their Consequences, Zoom app vulnerability
Several high-profile incidents highlight the real-world impact of Zoom vulnerabilities. For instance, reports of “Zoombombing” involved unauthorized individuals joining meetings and disrupting them with inappropriate content. This highlighted weaknesses in meeting security and the need for stronger access controls. Other incidents involved the exposure of user data due to vulnerabilities in data handling and encryption. These incidents led to increased scrutiny of Zoom’s security practices and prompted the company to implement significant improvements.
Vulnerability Exploitation Methods

Source: uctoday.com
Zoom, despite its popularity, isn’t immune to security flaws. Attackers constantly seek ways to exploit these vulnerabilities, ranging from simple social engineering tricks to sophisticated hacking techniques. Understanding these methods is crucial for protecting yourself and your organization.
Exploiting Zoom vulnerabilities often involves a combination of technical skills and social engineering tactics. Attackers might leverage publicly disclosed vulnerabilities or discover zero-day exploits, using them to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or disrupt Zoom services. This can range from gaining control of a user’s account to launching denial-of-service attacks affecting entire meetings.
Common Exploitation Techniques
Several methods are employed to exploit Zoom’s vulnerabilities. These include leveraging known software flaws, exploiting weak passwords, and using malicious plugins or add-ons. Furthermore, attackers can utilize phishing attacks or other social engineering techniques to trick users into compromising their accounts or systems. For instance, a vulnerability in a specific Zoom client version might allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code remotely if a user opens a specially crafted file. Another example is a malicious link embedded in a seemingly innocuous email, leading to a compromised account.
Social Engineering in Zoom Attacks
Social engineering plays a significant role in many Zoom-related attacks. Attackers often rely on deception and manipulation to trick users into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise their security. Common tactics include phishing emails disguised as official Zoom communications, fake Zoom support calls, or even cleverly crafted messages within Zoom chats themselves. These attacks exploit human psychology, leveraging urgency, fear, or trust to convince victims to comply. A typical scenario might involve an attacker posing as a Zoom support representative, requesting login credentials to “resolve a technical issue.”
Hypothetical Attack Scenario: Exploiting a Session Hijacking Vulnerability
Let’s imagine a scenario where a vulnerability allows session hijacking. This vulnerability, let’s say, resides in an older version of the Zoom client and allows an attacker to intercept a meeting ID and password if a user connects to a compromised Wi-Fi network.
- Compromised Network: The victim joins a meeting using a public Wi-Fi network unknowingly controlled by the attacker.
- Packet Capture: The attacker uses network sniffing tools to intercept the victim’s Zoom traffic, including the meeting ID and password (due to the vulnerability, these are transmitted insecurely).
- Session Hijacking: The attacker then uses the captured credentials to join the meeting as the victim, potentially gaining access to sensitive information shared during the meeting or disrupting the session.
- Data Exfiltration or Disruption: Once inside the meeting, the attacker could record the session, steal shared documents, or disrupt the meeting by spamming the chat or sharing inappropriate content.
This hypothetical scenario highlights the importance of using updated software, secure Wi-Fi networks, and practicing good security hygiene to mitigate the risk of such attacks. Remember, keeping your software updated and being vigilant against social engineering attempts are crucial in staying protected.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies: Zoom App Vulnerability
Protecting yourself and your organization from Zoom vulnerabilities requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing robust security measures, best practices, and diligent maintenance. Ignoring these steps can leave you exposed to significant risks, from data breaches to account hijacking. Let’s dive into the practical steps you can take to significantly bolster your Zoom security.
Effective mitigation strategies go beyond simply updating the app. They involve a holistic approach to account security, meeting management, and overall digital hygiene. By implementing these measures, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to Zoom-related attacks and protect sensitive information.
Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Employing strong, unique passwords is fundamental. Avoid easily guessable passwords like “password123” or your birthday. Instead, opt for complex passwords combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Further enhancing security is the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or email, in addition to your password. This makes it exponentially harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they obtain your password. Consider using a password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords.
Secure Meeting Settings
Before initiating a Zoom meeting, carefully review and adjust the security settings. Enable the waiting room feature to control who enters the meeting, preventing uninvited participants from joining. Disable screen sharing for participants unless absolutely necessary to prevent unauthorized access and the potential sharing of sensitive information. Consider using a password for your meetings, particularly for sensitive discussions or meetings involving confidential information. Utilize the “Remove Participant” function to swiftly eject disruptive or unauthorized individuals from your meeting.
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Staying current with the latest Zoom updates is crucial. Zoom regularly releases patches addressing newly discovered vulnerabilities. Failing to update your application leaves your system exposed to known exploits. Implement a system for automatic updates, if available, to ensure your Zoom application is always running the most secure version. For organizations, establish a robust patch management system to efficiently deploy updates across all devices and accounts. This proactive approach is vital in minimizing the risk of successful attacks.
Security Awareness Training
Educating users about potential threats and best practices is paramount. Conduct regular security awareness training to inform individuals about phishing scams, malicious links, and other social engineering tactics often used to exploit Zoom vulnerabilities. Train employees to recognize and report suspicious emails or messages. Encourage the use of strong passwords and the importance of MFA. By fostering a culture of security awareness, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of successful attacks.
Action Checklist for Individuals and Organizations
The following checklist summarizes the key actions individuals and organizations should take to reduce their vulnerability to Zoom attacks. Consistent adherence to these practices is essential for maintaining a secure environment.
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication.
- Review and adjust Zoom meeting security settings before each meeting.
- Keep your Zoom application updated with the latest security patches.
- Implement a robust patch management system for organizations.
- Conduct regular security awareness training for users.
- Report suspicious activity to Zoom support immediately.
- Regularly review and update your Zoom account settings and permissions.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments in emails or messages.
Zoom’s Security Response and Patching Process
Zoom’s security response and patching process has been under intense scrutiny since its meteoric rise to prominence. The platform’s rapid growth highlighted the critical need for a robust and responsive security infrastructure capable of handling a massive user base and the inevitable influx of security vulnerabilities. Understanding how Zoom identifies, addresses, and communicates these issues is crucial for assessing its overall security posture.
Zoom employs a multi-faceted approach to identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities. This includes a combination of internal security research, bug bounty programs, and external vulnerability reporting. The company actively encourages security researchers to report vulnerabilities responsibly, often offering financial rewards for credible findings. Internal teams conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to proactively identify weaknesses in the platform’s architecture and codebase. This proactive approach aims to detect and mitigate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
Zoom’s Security Response Time Compared to Competitors
Direct comparison of response times across various video conferencing platforms is difficult due to a lack of publicly available, standardized data on vulnerability disclosure timelines. However, anecdotal evidence and publicly reported incidents suggest that Zoom’s response time has varied considerably over time. Initially, the company faced criticism for relatively slow responses to some reported vulnerabilities. However, in response to this criticism and increased scrutiny, Zoom has reportedly invested significantly in improving its security response processes, aiming for faster identification, patching, and communication to users. A direct comparison would require detailed, publicly accessible information from all competing platforms, which is currently not consistently available.
Effectiveness of Zoom’s Patching Process
The effectiveness of Zoom’s patching process is a complex issue. While the company has made significant improvements in its response time and communication, the ultimate effectiveness depends on several factors, including the speed and reach of patch deployment, user adoption rates, and the sophistication of potential attacks. A rapid patch release is only effective if users promptly update their software. Furthermore, the effectiveness is also dependent on the thoroughness of the patch itself; a poorly implemented patch might not fully address the vulnerability, leaving the system susceptible to future attacks. While Zoom has improved, the continuous evolution of attack methods means that no patching process is foolproof. The effectiveness is an ongoing process of improvement and adaptation.
Zoom’s Communication of Security Updates and Patches
Zoom communicates security updates and patches to its users through various channels, including in-app notifications, email alerts, and updates to its security advisory page on its website. These communications generally include details about the vulnerabilities addressed, the impact of the vulnerabilities, and instructions on how to update the software to the patched version. The clarity and timeliness of these communications have also improved over time, though there is always room for improvement in ensuring all users receive and understand the updates. For example, a significant update might trigger a pop-up notification within the app itself, urging users to immediately update. The effectiveness of this communication strategy relies on users actively checking for updates and responding promptly to notifications.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Exploiting vulnerabilities in widely used applications like Zoom carries significant legal and ethical weight. The consequences extend beyond mere technical breaches, impacting individuals, organizations, and the broader societal trust in digital platforms. Understanding these implications is crucial for developers, users, and lawmakers alike.
The legal ramifications of exploiting Zoom app vulnerabilities are multifaceted and depend heavily on the context of the exploitation. Malicious actors face potential prosecution under various laws, including those related to computer fraud and abuse, unauthorized access, data theft, and violations of privacy. The severity of the penalties can vary greatly depending on the nature of the vulnerability, the extent of the damage caused, and the intent of the perpetrator. For instance, exploiting a vulnerability to gain access to sensitive medical information would likely result in far more severe penalties than exploiting a vulnerability to merely disrupt service.
Legal Ramifications of Exploiting Zoom Vulnerabilities
Exploiting Zoom vulnerabilities can lead to various legal repercussions, depending on the jurisdiction and the specific actions taken. These range from civil lawsuits for damages to criminal charges for malicious activities. The penalties can include hefty fines, imprisonment, and reputational damage. For example, a hacker who gains unauthorized access to user data and sells it on the dark web could face serious criminal charges under laws pertaining to data theft and identity theft. Similarly, a company that fails to adequately address known vulnerabilities and suffers a data breach could face significant civil liability for negligence.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Zoom Security Tools
The development and use of Zoom security tools raise several ethical considerations. Developers have a responsibility to ensure that their tools are secure and do not introduce new vulnerabilities. They must also consider the potential for misuse of their tools by malicious actors. Users, in turn, have an ethical obligation to use Zoom and its security features responsibly, respecting the privacy and security of others. The ethical implications become especially acute when considering the use of security tools for surveillance or monitoring without proper authorization or transparency.
Responsibilities of Zoom and its Users Regarding Data Privacy and Security
Zoom, as a platform provider, bears a significant responsibility for ensuring the privacy and security of its users’ data. This includes proactively identifying and patching vulnerabilities, implementing robust security measures, and being transparent with users about potential risks. Users, on the other hand, also have a responsibility to protect their own data by using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious about sharing sensitive information. Both Zoom and its users need to actively participate in maintaining a secure and trustworthy online environment.
Comparison of Legal Frameworks in Different Jurisdictions
Different jurisdictions have varying legal frameworks for addressing Zoom security breaches. A consistent approach across borders is lacking, creating complexities for both companies and users.
- United States: Relies on a patchwork of federal and state laws, including the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), various state data breach notification laws, and common law principles of negligence. Enforcement and penalties vary widely.
- European Union (GDPR): The General Data Protection Regulation imposes stringent requirements on data processing, including security measures and notification of breaches. Non-compliance can result in significant fines.
- China: China’s Cybersecurity Law and other regulations place a strong emphasis on data localization and security. Companies operating in China face specific obligations regarding data handling and security.
- United Kingdom: The UK’s Data Protection Act 2018, aligned with GDPR principles, sets out requirements for data protection and security, with similar penalties for non-compliance.
Future Trends in Zoom Security
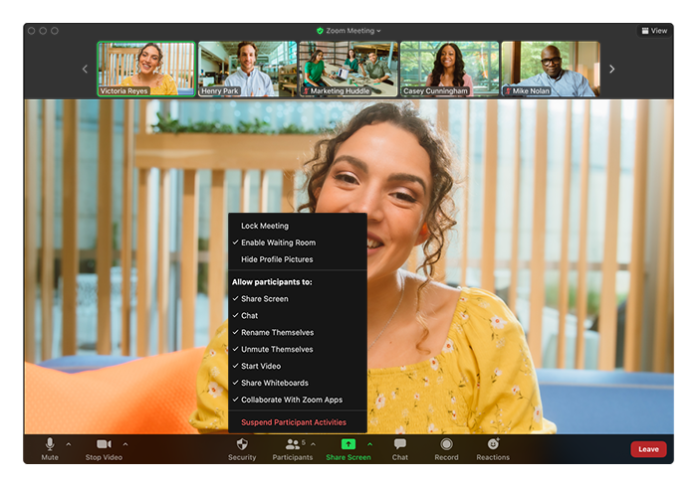
Source: zoom.us
Predicting the future of cybersecurity is a tricky business, akin to forecasting the weather in a hurricane. However, based on current trends and emerging threats, we can make some educated guesses about the evolution of Zoom’s security landscape. The constant arms race between attackers and defenders means Zoom, and other video conferencing platforms, will need to adapt and innovate to stay ahead of the curve.
Zoom’s future security will likely hinge on a multi-pronged approach, encompassing advancements in AI-powered threat detection, enhanced encryption protocols, and a greater emphasis on user education and responsible usage. We’ll see a shift towards more proactive security measures, moving beyond simply patching vulnerabilities to anticipating and preventing attacks before they happen.
Advanced Threat Detection and Response
The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks necessitates a move beyond traditional signature-based detection. AI and machine learning will play a crucial role in identifying anomalies and predicting potential threats in real-time. This will involve analyzing vast amounts of data from user activity, network traffic, and application logs to pinpoint suspicious behavior before it escalates into a full-blown breach. Imagine a system that can detect unusual screen sharing patterns or unusual audio activity, flagging potential compromise attempts before any sensitive data is exposed. This proactive approach would greatly enhance Zoom’s ability to identify and neutralize threats before they cause significant damage.
Post-Quantum Cryptography and Enhanced Encryption
The advent of quantum computing poses a significant threat to current encryption standards. Zoom will need to proactively transition to post-quantum cryptography algorithms that can withstand attacks from quantum computers. This will involve a significant overhaul of its encryption infrastructure, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of communications in a post-quantum world. A successful transition will require extensive testing and validation to ensure compatibility and performance across different devices and platforms. Failure to adapt to post-quantum cryptography could leave Zoom vulnerable to devastating attacks in the future.
Emerging Threats: AI-Powered Attacks and Deepfakes
The future isn’t just about stronger defenses; it’s also about anticipating new attack vectors. AI-powered attacks, which leverage machine learning to automate and scale attacks, pose a significant threat. These attacks can adapt and learn, making them more difficult to detect and defend against. Additionally, deepfakes—synthetic media that can convincingly impersonate individuals—could be used to compromise Zoom meetings, potentially leading to fraud, misinformation, or social engineering attacks. Imagine a scenario where a deepfake of a CEO authorizes a large financial transaction during a seemingly legitimate Zoom meeting. The consequences could be catastrophic.
Hypothetical Future Vulnerability Scenario
Imagine a future Zoom vulnerability exploiting a newly discovered flaw in the platform’s screen-sharing functionality. A sophisticated attacker could leverage this vulnerability to inject malicious code into a participant’s system during a seemingly harmless screen share. This malicious code could gain unauthorized access to the victim’s files, credentials, or even control their system remotely. The impact could be widespread, affecting thousands of users and potentially leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage for Zoom. The visual representation would depict a seemingly innocuous screen share, subtly transitioning into a malicious overlay, unbeknownst to the participants. The overlay would represent the silent execution of malicious code, ultimately leading to compromised systems. This illustrates the need for robust security measures to mitigate such emerging threats.
Outcome Summary

Source: uctoday.com
Navigating the world of Zoom app vulnerabilities requires a multi-faceted approach. While Zoom continuously works to improve its security, individual users and organizations bear a significant responsibility. Staying updated on security patches, adopting robust security practices, and being vigilant against social engineering attempts are crucial. The future of Zoom’s security hinges on a collaborative effort—a constant vigilance that protects both individual privacy and the integrity of our digital interactions. The stakes are high, but with awareness and proactive measures, we can minimize the risks and navigate this digital landscape with greater confidence.





