Citrix virtual apps desktops rce – Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops RCE: The phrase alone sends shivers down the spines of IT admins everywhere. This vulnerability, allowing remote code execution, isn’t just a theoretical threat; it’s a real-world danger that’s repeatedly exploited to gain unauthorized access and wreak havoc on systems. We’re diving deep into the nitty-gritty, exploring the techniques used, the devastating consequences, and most importantly, how to protect your network from this digital menace.
We’ll dissect the various attack vectors, from cleverly crafted malicious code to exploiting known vulnerabilities. We’ll examine real-world examples, showing you exactly how these attacks unfold and the damage they inflict. But fear not, we’re not just here to highlight the problem; we’ll arm you with the knowledge and strategies to effectively mitigate the risk and secure your Citrix environment. This isn’t just about patching; it’s about building a robust, layered defense against this persistent threat.
Vulnerability Overview
Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, while offering powerful virtualization capabilities, has unfortunately been plagued by several critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities over the years. These vulnerabilities allow attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code on vulnerable Citrix servers, potentially compromising the entire infrastructure and sensitive data residing within. Understanding the nature of these vulnerabilities, their impact, and the steps taken to mitigate them is crucial for maintaining a secure virtualized environment.
The Citrix RCE vulnerabilities typically stem from flaws in the Citrix ADC (Application Delivery Controller) and Gateway components, which are essential for managing and accessing virtual applications and desktops. Attackers can exploit these weaknesses by sending specially crafted requests to vulnerable components, leading to the execution of malicious code on the server. This allows them to gain complete control, potentially installing malware, stealing data, or disrupting services. The exact method of exploitation varies depending on the specific vulnerability, but often involves manipulating network protocols or leveraging flaws in the server’s processing of incoming requests.
Potential Impact of Successful Exploit
A successful exploitation of a Citrix RCE vulnerability can have devastating consequences. The attacker gains complete control of the affected server, allowing them to perform a wide range of malicious actions. This could include: data breaches, exfiltration of sensitive corporate information (customer data, financial records, intellectual property); system compromise, installing ransomware or other malware to encrypt or destroy data, disrupt operations, or establish a persistent backdoor for future attacks; network compromise, using the compromised server as a launching point for attacks against other systems within the network; and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, rendering the virtual apps and desktops inaccessible to legitimate users. The impact can extend beyond the immediate server, affecting the entire organization’s operations and reputation.
Real-World Incidents Involving Citrix RCE Vulnerabilities
Several high-profile incidents have demonstrated the real-world impact of Citrix RCE vulnerabilities. While specific details are often kept confidential for security reasons, reports have surfaced of organizations experiencing significant data breaches and operational disruptions following successful exploits. For example, some attacks have leveraged these vulnerabilities to gain initial access to a network, leading to wider compromises involving other systems and data. The scale of these breaches often depends on the attacker’s skills and objectives, but the potential for widespread damage is significant. The lack of timely patching is frequently cited as a contributing factor in these incidents.
Citrix RCE Vulnerabilities: CVE Table
Understanding the specific vulnerabilities is crucial for effective mitigation. The following table summarizes some key CVEs associated with Citrix RCE vulnerabilities, their severity, and recommended remediation steps. Note that this is not an exhaustive list, and new vulnerabilities are discovered periodically. Always refer to the official Citrix security advisories for the most up-to-date information.
| CVE ID | Severity | Description (Simplified) | Remediation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-XXXX-YYYY (Example) | Critical | Vulnerability in component X allows RCE. | Apply the latest Citrix security updates. |
| CVE-ZZZZ-WWWW (Example) | High | Improper input validation leads to RCE. | Upgrade to the latest version of Citrix ADC and Gateway. |
| CVE-AAAA-BBBB (Example) | Medium | Vulnerability in a less critical component. | Apply the relevant patch from Citrix. |
| CVE-CCCC-DDDD (Example) | Low | Minor vulnerability; potential for RCE under specific circumstances. | Monitor for updates and apply patches as released. |
Exploit Techniques
The Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops RCE vulnerability, once exploited, can grant attackers complete control over the affected system. Understanding the methods used is crucial for effective defense. These techniques often leverage vulnerabilities in the Citrix components to execute arbitrary code, leading to data breaches, system compromise, and potentially wider network infiltration.
Exploiting the vulnerability typically involves manipulating specific components within the Citrix infrastructure. Attackers might leverage flaws in web interfaces, insecure configurations, or vulnerabilities in the underlying operating system. This often requires a degree of technical expertise and knowledge of the target environment.
Common Exploitation Methods
Several methods exist for exploiting Citrix RCE vulnerabilities. These can range from simple, readily available exploits to more sophisticated attacks tailored to specific configurations. The success of an attack often hinges on the attacker’s ability to bypass security measures and execute malicious code within the Citrix environment.
Steps in a Typical Attack Scenario
A typical attack might begin with reconnaissance to identify vulnerable Citrix servers. The attacker would then craft an exploit targeting a known vulnerability, often using publicly available tools or custom-built scripts. Successful exploitation involves injecting malicious code, often in the form of a shell command or a payload that downloads and executes further malware. This grants the attacker remote code execution capabilities, allowing them to control the compromised system. Finally, the attacker might escalate privileges, establish persistence, and exfiltrate sensitive data.
Examples of Malicious Code
The malicious code used in a Citrix RCE exploit can vary widely depending on the attacker’s goals. A simple example might involve a command to execute a shell, providing a command-line interface to the compromised system. More complex attacks might involve downloading and executing malware that steals credentials, encrypts data (ransomware), or establishes a backdoor for persistent access. For instance, a malicious payload could be a PowerShell script designed to download and execute a remote access trojan (RAT), giving the attacker persistent control. Another example could be a command to execute a binary that installs a keylogger, capturing user input and potentially stealing sensitive information like passwords and credit card details.
Hypothetical Attack Scenario
Imagine a scenario where an attacker discovers a vulnerable Citrix server exposed to the internet. Using a publicly available exploit script, the attacker sends a specially crafted request to the server. This request triggers the vulnerability, allowing the attacker to inject a PowerShell script that downloads and executes a Meterpreter payload. This payload gives the attacker complete control over the server, allowing them to browse files, execute commands, and potentially move laterally within the network to compromise other systems. The attacker could then install a backdoor for future access and exfiltrate sensitive data before the compromise is detected. The entire attack might be completed within minutes, leaving little trace of the attacker’s presence.
Mitigation Strategies
Successfully patching and securing your Citrix environment against Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities requires a multi-layered approach. Ignoring even one aspect can leave your system vulnerable. This section details the crucial steps to minimize your risk.
Addressing Citrix RCE vulnerabilities demands a proactive and comprehensive strategy, going beyond simply applying patches. It necessitates a holistic review of your security posture, encompassing both technical controls and organizational best practices.
Security Patches and Updates
Promptly applying security patches and updates issued by Citrix is paramount. These updates often directly address known vulnerabilities, including those that could lead to RCE. Citrix regularly releases security bulletins detailing the vulnerabilities and the corresponding patches. A robust patch management system, including automated deployment and testing in a non-production environment before rollout to production, is essential. Failing to keep your Citrix infrastructure up-to-date significantly increases your exposure to exploitation. For example, the delay in patching a critical vulnerability discovered in a previous version of Citrix ADC allowed attackers to compromise systems globally, highlighting the severity of neglecting updates.
Securing Citrix Environments
Beyond patching, numerous best practices significantly enhance the security of your Citrix environment. These include implementing strong password policies, enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA), regularly auditing user access rights, and utilizing network segmentation to isolate sensitive resources. Regular security assessments and penetration testing can identify vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. Employing a least privilege model ensures that users only have the access necessary to perform their tasks, minimizing the potential damage from a compromised account. For instance, implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it considerably harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access even if they obtain credentials.
Mitigation Techniques: Network Segmentation and Access Controls
Network segmentation isolates different parts of your network, limiting the impact of a successful breach. If one segment is compromised, the attacker’s lateral movement is restricted. This contrasts with a flat network architecture where a successful breach can lead to widespread compromise. Access controls, such as role-based access control (RBAC), restrict access to resources based on user roles and responsibilities. RBAC prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data or systems. A robust combination of network segmentation and access controls minimizes the blast radius of a successful attack, containing the damage and protecting critical assets. For example, separating your Citrix environment from other critical systems prevents an attacker from using a Citrix compromise as a springboard to attack other parts of your infrastructure.
Security Controls Implementation
Implementing a comprehensive suite of security controls is vital for mitigating the risk of Citrix RCE attacks.
This requires a coordinated effort involving several key areas:
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Identify vulnerabilities proactively.
- Robust Patch Management System: Ensure timely application of security updates.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security to user accounts.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate sensitive systems and data.
- Least Privilege Access Control: Restrict user access to only necessary resources.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Monitor network traffic for malicious activity.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Centralize security logs and alerts for better threat detection and response.
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Educate users about phishing and other social engineering attacks.
Detection and Response
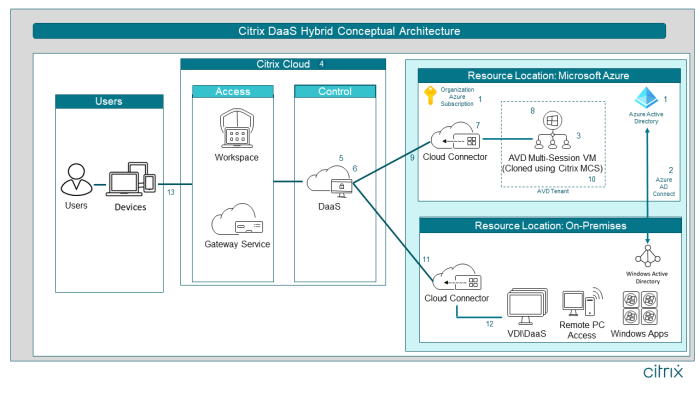
Source: citrix.com
Detecting and responding to a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops Remote Code Execution (RCE) attack requires a proactive and layered security approach. Early detection minimizes damage and facilitates a swift recovery. A robust incident response plan is crucial for effective remediation and preventing future attacks.
Knowing what to look for and having a clear plan of action is paramount in mitigating the impact of an RCE exploit. This section Artikels methods for identifying suspicious activity, responding to successful attacks, and leveraging security tools to enhance your defenses.
Suspicious Activity Detection Methods
Identifying suspicious activity hinges on monitoring key system logs and network traffic for anomalies. Unusual login attempts, unexpected process executions, or modifications to critical system files are all red flags. Continuous monitoring is vital, as attackers often attempt to remain undetected for as long as possible. Analyzing system logs for unauthorized commands, unusual file access patterns, and unexpected data exfiltration attempts provides critical insights into potential RCE activity. Furthermore, monitoring network traffic for unusual outbound connections or large data transfers can also help identify compromised systems.
Incident Response Steps
Responding to a successful RCE attack demands a structured approach. The speed and effectiveness of your response directly impact the extent of the damage. A well-defined incident response plan, tested through regular drills, is essential.
- Isolate the affected system: Immediately disconnect the compromised system from the network to prevent further lateral movement and data exfiltration.
- Secure evidence: Create forensic images of the affected system’s hard drives and memory to preserve evidence for later analysis and investigation.
- Identify the extent of the compromise: Determine which systems have been impacted and what data may have been accessed or exfiltrated. This may involve analyzing system logs, network traffic, and other relevant data sources.
- Remediate the vulnerability: Patch the exploited vulnerability in Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops and any other affected systems. This includes applying the latest security updates and configurations.
- Restore affected systems: Restore systems from backups or rebuild them from scratch, ensuring that all security measures are in place before restoring data.
- Monitor for further attacks: Continuously monitor systems for any further suspicious activity and implement enhanced security measures to prevent future attacks.
- Conduct a post-incident review: Analyze the incident to identify weaknesses in your security posture and implement corrective measures to prevent similar attacks in the future.
Security Tools for Detection and Prevention
Several security tools can significantly enhance your ability to detect and prevent RCE attacks. These tools provide advanced monitoring capabilities, real-time threat detection, and automated response mechanisms. Examples include Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS), and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions. A well-integrated security stack is crucial for comprehensive protection.
- SIEM systems: These systems aggregate logs from various sources to provide a centralized view of security events. They can help detect anomalies and suspicious activities indicative of RCE attempts.
- IDS/IPS: These systems monitor network traffic for malicious activity, including attempts to exploit vulnerabilities. They can block or alert on suspicious traffic patterns.
- EDR solutions: These solutions provide advanced endpoint protection by monitoring system activity for malicious behavior. They can detect and respond to RCE attempts in real-time.
- Vulnerability scanners: Regularly scanning your systems for known vulnerabilities helps identify and address potential weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. Examples include Nessus, OpenVAS, and QualysGuard.
Vulnerability Analysis: Citrix Virtual Apps Desktops Rce
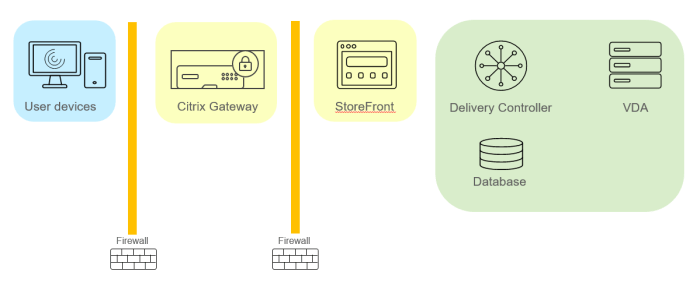
Source: citrix.com
Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops RCE vulnerabilities stem from flaws in the software’s handling of user input and its interaction with the underlying operating system. These vulnerabilities often exploit weaknesses in how the application processes requests, leading to unintended code execution within the server’s context. Understanding the root causes requires a deep dive into the specific vulnerabilities, which can vary significantly depending on the affected version and component.
The core mechanism allowing remote code execution usually involves manipulating data sent to the Citrix server. A malicious actor might craft a specially designed request, leveraging a known vulnerability in a specific component, such as a web interface or a back-end service. This crafted request might contain malicious code, or it might trigger the execution of existing code in an unexpected way, granting the attacker control. Successful exploitation typically requires a chain of vulnerabilities or the exploitation of a single critical vulnerability with sufficient privileges. For example, an attacker might exploit a vulnerability in a web application to gain initial access, then escalate privileges to execute arbitrary code on the server.
Underlying Causes of the Vulnerability
Citrix vulnerabilities often arise from insecure coding practices, insufficient input validation, and inadequate memory management. Failure to properly sanitize user input allows attackers to inject malicious code into the system. Memory management flaws, such as buffer overflows or use-after-free errors, can also be exploited to overwrite critical memory regions and inject malicious instructions. Furthermore, outdated or poorly configured components within the Citrix environment can introduce additional attack vectors.
How the Vulnerability Enables Remote Code Execution
The ability to execute arbitrary code remotely allows an attacker complete control over the affected Citrix server. This control can range from simple data theft to complete system compromise, potentially impacting all users and data within the virtual environment. A successful attack often involves several stages: initial exploitation of a vulnerability to gain access, privilege escalation to obtain higher-level permissions, and finally, the execution of malicious code to achieve the attacker’s objective. This code could be used to install malware, steal sensitive data, launch further attacks against other systems, or disrupt services.
Comparison to Similar RCE Vulnerabilities
Citrix RCE vulnerabilities share similarities with RCE vulnerabilities found in other enterprise software. Many follow the pattern of insecure handling of user input or flaws in component interaction. For example, vulnerabilities in web servers like Apache or IIS, or in database systems like Oracle or MySQL, have historically shown similar exploitation patterns. In each case, the root cause often lies in inadequate security measures during the software development lifecycle. The severity, however, can vary depending on the specific application, its architecture, and the level of access granted to the attacker.
Factors Contributing to Vulnerability Severity
Several factors influence the severity of a Citrix RCE vulnerability:
The impact of a successful exploitation is crucial. A vulnerability that allows an attacker to steal sensitive data is more severe than one that only allows for denial-of-service attacks. The ease of exploitation, measured by the technical skills and resources required, also plays a critical role. A vulnerability easily exploitable by automated tools is far more dangerous than one requiring advanced skills and custom-crafted exploits. The availability of exploit code publicly available on the internet makes a vulnerability significantly more dangerous, as it lowers the barrier to entry for malicious actors. Finally, the affected Citrix environment’s size and the amount of sensitive data it manages directly impacts the potential damage from a successful breach. A larger, more data-rich environment will suffer more significant consequences.
Impact Assessment
A successful Remote Code Execution (RCE) exploit targeting Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops can have devastating consequences for an organization, extending far beyond simple system downtime. The impact ripples across operational efficiency, financial stability, and brand reputation, potentially leading to significant long-term repercussions. Understanding the potential ramifications is crucial for effective risk management and proactive mitigation.
The severity of the impact hinges on several factors, including the attacker’s goals, the sensitivity of the compromised data, and the organization’s response capabilities. However, the potential for widespread damage is undeniable, making robust security measures paramount.
Financial Losses
A successful RCE attack can lead to substantial financial losses through various channels. Data breaches can result in hefty fines for non-compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA. The cost of incident response, including forensic investigations, system recovery, and legal fees, can quickly escalate. Furthermore, loss of productivity due to system downtime and the disruption of business operations can significantly impact revenue streams. Consider a hypothetical scenario where a major financial institution suffers a breach exposing customer financial data. The resulting fines, legal battles, and reputational damage could easily cost tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. The cost of rebuilding trust with customers after such a breach is also substantial and difficult to quantify.
Reputational Damage
Beyond the direct financial impact, a successful RCE attack can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Public disclosure of a data breach, especially one involving sensitive customer information, can erode public trust and negatively impact brand loyalty. This reputational damage can translate into lost customers, decreased investment, and difficulty attracting and retaining talent. For example, a healthcare provider experiencing a data breach exposing patient medical records would face intense scrutiny from regulators, the media, and the public, potentially leading to a significant loss of patient trust and long-term damage to its reputation.
Operational Disruption
The disruption of critical business operations is another significant consequence of a successful RCE attack. Compromised systems can lead to downtime, hindering productivity and potentially causing significant delays in critical business processes. The inability to access essential data or applications can disrupt workflows, impacting deadlines and potentially jeopardizing ongoing projects. Imagine a manufacturing company whose production systems are compromised. The resulting downtime could halt production lines, leading to lost revenue and unmet customer orders, potentially impacting supply chains and long-term business viability.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Small Business Attack
Imagine a small accounting firm relying heavily on Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops for client data access and internal operations. A successful RCE attack compromises their system, granting attackers access to sensitive client tax information and financial records. The attackers exfiltrate this data and demand a ransom for its return. The firm faces substantial financial losses due to the ransom payment, legal fees associated with notifying affected clients, and the cost of rebuilding their IT infrastructure. Furthermore, the breach severely damages their reputation, leading to a loss of clients and difficulty attracting new business. This scenario highlights the vulnerability of even smaller organizations to the significant impact of a successful RCE exploit.
Future Considerations
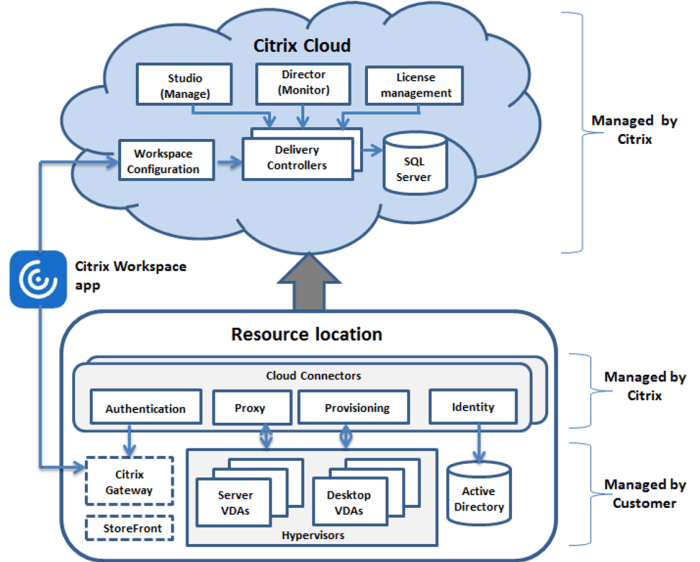
Source: citrix.com
The ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats necessitates a proactive approach to securing Citrix environments. While current mitigation strategies address known vulnerabilities, the inherent complexity of virtualized environments, coupled with the continuous innovation in attack techniques, means future vulnerabilities are inevitable. Understanding these potential weaknesses and implementing robust preventative measures is crucial for maintaining a secure digital infrastructure.
Predicting specific future vulnerabilities is inherently challenging, but by analyzing current trends and attack vectors, we can identify areas of heightened risk and prioritize security enhancements. The focus should shift from reactive patching to a more proactive, predictive security posture.
Potential Future Vulnerability Types
Citrix’s continued development and integration of new features, such as cloud-based services and enhanced collaboration tools, introduce new attack surfaces. These additions, while beneficial for productivity, often bring unforeseen security risks. For instance, vulnerabilities could emerge in the integration points between different Citrix components or between Citrix and third-party applications. Furthermore, the increasing reliance on APIs and microservices within the Citrix architecture creates opportunities for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in these interfaces. Improperly configured or insecure APIs could allow unauthorized access or data breaches. Zero-day exploits targeting newly introduced features are also a significant concern. A real-world example is the recent increase in attacks leveraging vulnerabilities in newly released software updates, highlighting the need for thorough security testing before deployment.
Improved Security Measures: Enhanced Authentication and Authorization, Citrix virtual apps desktops rce
Strengthening authentication and authorization mechanisms is paramount. Moving beyond traditional password-based authentication to multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential. Implementing robust access control lists (ACLs) and regularly auditing user privileges can limit the impact of successful breaches. Context-aware authentication, which considers factors like user location and device security posture, adds an extra layer of protection. Imagine a scenario where a user attempts to access sensitive data from an unfamiliar location; context-aware authentication could flag this suspicious activity and prevent unauthorized access. Furthermore, integrating advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying anomalous behavior patterns is crucial for proactively mitigating potential threats.
Enhancing Citrix Environment Security: Proactive Vulnerability Management
A proactive vulnerability management program is essential. This involves regularly scanning for vulnerabilities using automated tools, promptly patching identified weaknesses, and rigorously testing patches before deployment to avoid unintended consequences. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments should be conducted to identify weaknesses in the Citrix infrastructure. These assessments should cover not only the Citrix components themselves but also the underlying infrastructure, such as the network, operating systems, and databases. Maintaining up-to-date security information and event management (SIEM) systems is critical for detecting and responding to security incidents in a timely manner.
Proactive Security Monitoring and Vulnerability Management Plan
A comprehensive plan should incorporate continuous monitoring of Citrix systems for suspicious activity. This includes real-time log analysis, security information and event management (SIEM) integration, and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS). Regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing should be scheduled and documented, with a clearly defined process for addressing identified vulnerabilities. This plan must also include a robust incident response plan that Artikels steps to be taken in the event of a security breach, including containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the Citrix environment and evolving threat landscapes. Regular employee security awareness training is also crucial to mitigate the risk of human error, a common cause of security breaches. The training should cover topics such as phishing awareness, password security, and safe browsing practices.
Final Wrap-Up
So, there you have it – a comprehensive look at the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops RCE vulnerability. While the potential impact is significant, the good news is that proactive measures, robust security practices, and staying updated on the latest patches can significantly reduce your risk. Remember, it’s not a matter of *if* but *when* you’ll face a security threat. By understanding the landscape and implementing the right defenses, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability and safeguard your organization’s valuable data and reputation.





