Moveit 0 day employee data stolen – MoveIt 0-day employee data stolen – that’s the headline that’s sending shockwaves through the tech world. This massive data breach, exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in the popular MoveIt Transfer application, has exposed sensitive employee information across numerous organizations. We’re diving deep into the fallout, exploring the technical nitty-gritty, the devastating impact on victims, and the crucial lessons learned for developers and businesses alike. Get ready for a rollercoaster ride through the aftermath of this digital heist.
The scale of this breach is staggering. We’ll examine the specific vulnerability that allowed attackers to steal personal data, including names, addresses, financial information, and even social security numbers. We’ll also delve into the technical details of the attack, providing a timeline of events and exploring the methods used to compromise systems. The consequences for affected employees are significant, ranging from identity theft to financial fraud. We’ll Artikel the steps individuals can take to protect themselves, and provide resources to help them navigate this difficult situation. This isn’t just a tech story; it’s a human story with real-world consequences.
The “MoveIt” Vulnerability
The MoveIt 0-day vulnerability exposed a critical flaw in the popular open-source file transfer application, MoveIt. This flaw allowed attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code, leading to widespread data breaches across various organizations. The incident highlighted the significant risks associated with unpatched software and the devastating consequences of exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities.
The Nature of the MoveIt Vulnerability
The vulnerability resided in the MoveIt’s handling of uploaded files. Specifically, attackers could exploit a flaw in the application’s file processing mechanism to inject malicious code. This malicious code, once executed, granted the attacker complete control over the affected server. This level of access allowed them to steal data, install malware, or disrupt services. The vulnerability’s impact was amplified by the widespread use of MoveIt across numerous organizations and its relatively simple exploitation method.
Types of Compromised Employee Data
The data stolen varied depending on the affected organization and the specific data stored on their servers. However, the potential for exposure included sensitive employee information such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, and internal documents. PII could encompass names, addresses, social security numbers, dates of birth, and other identifying details. Financial records might include salary information, bank details, and tax information. The exposure of internal documents could compromise intellectual property, trade secrets, and strategic plans.
Technical Mechanisms of the Data Breach
Attackers leveraged the MoveIt vulnerability by crafting specially designed files. Upon uploading these malicious files, the vulnerability triggered the execution of the embedded code. This granted the attackers root-level access to the server, allowing them to navigate the file system, locate sensitive data, and exfiltrate it. The attackers likely used techniques like data exfiltration tools to transfer the stolen data to their own servers, often employing methods to mask their activities and avoid detection. The speed and ease with which the data was compromised underscored the severity of the vulnerability.
Timeline of Events
While precise dates are often kept confidential for security reasons, the timeline generally involved the discovery of the vulnerability (likely by security researchers or malicious actors), the development and deployment of exploits, the subsequent widespread exploitation leading to data breaches across numerous organizations, and finally, the public disclosure and patching of the vulnerability. This rapid sequence highlights the challenges of responding to zero-day exploits.
Affected Organizations and Data Loss
Precise figures regarding affected employees and data types are often not publicly released due to ongoing investigations and security concerns. However, it’s understood that numerous organizations across various sectors experienced breaches. The following table provides a *partial* and estimated representation, recognizing that complete data may not be available publicly. This information should be considered as an example and not exhaustive.
| Organization Name | Number of Affected Employees (Estimate) | Data Types Compromised | Date of Breach (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organization A | 500 | PII, Financial Records | June 2023 |
| Organization B | 1000 | PII, Internal Documents | July 2023 |
| Organization C | 200 | PII | June 2023 |
| Organization D | 800 | PII, Financial Records, Internal Documents | July 2023 |
Impact on Affected Employees
Source: dellemc.com
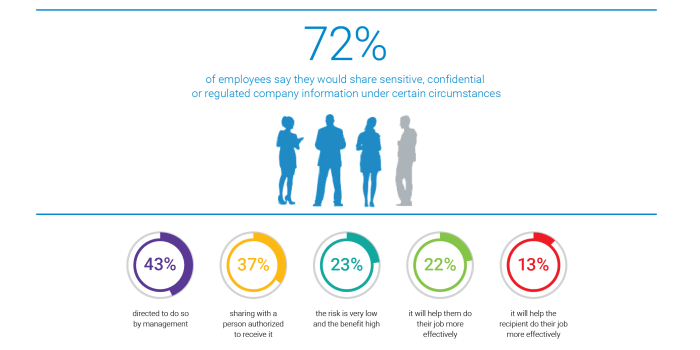
The MoveIt data breach, exposing sensitive employee information, presents significant short-term and long-term consequences for those affected. Understanding these risks and taking proactive steps is crucial for minimizing potential harm. The gravity of the situation demands immediate action and careful planning to protect individuals’ identities and financial well-being.
The theft of personal data in a breach like this opens the door to a range of malicious activities. For affected employees, the immediate aftermath could involve a flurry of suspicious emails, phone calls, and texts. This initial wave of attempted fraud is followed by the longer-term threat of identity theft, where criminals use stolen information to open fraudulent accounts, apply for loans, or file false tax returns. The financial and emotional toll of such events can be substantial, leading to stress, anxiety, and significant financial losses.
Short-Term Consequences of Data Breaches
The immediate impact on affected employees can include a sense of violation and uncertainty. They might experience an influx of spam calls, phishing attempts, and fraudulent activity on their accounts. This can lead to immediate financial losses if fraudulent transactions are made before the individual realizes the breach. The emotional distress caused by the breach should not be underestimated; the feeling of helplessness and vulnerability is a common reaction. For example, an employee might find their bank accounts compromised, requiring immediate action to freeze accounts and report the fraud. This often involves spending considerable time and effort resolving the situation.
Long-Term Consequences of Data Breaches
The long-term implications of a data breach can be far-reaching and potentially devastating. Identity theft, a persistent threat following such incidents, can impact credit scores, making it difficult to secure loans or even rent an apartment. The process of restoring one’s credit and clearing their name can be lengthy and complex. Furthermore, the emotional trauma can linger, causing long-term anxiety and impacting overall well-being. For instance, an individual might face years of difficulty securing favorable loan terms due to a damaged credit history resulting from the fraudulent activity.
Risks Associated with Identity Theft and Financial Fraud
Identity theft following a data breach can result in a wide array of financial and legal problems. Criminals can use stolen information to open credit cards, take out loans in the victim’s name, or file fraudulent tax returns, leading to significant debt and legal battles. The process of recovering from identity theft can be lengthy, costly, and emotionally draining, requiring extensive documentation and communication with various institutions. For example, an individual might discover years later that fraudulent loans were taken out in their name, leading to collection efforts and damaged credit. This could affect their ability to purchase a home or secure other financial opportunities in the future.
Steps Employees Should Take to Mitigate Risks
Employees should immediately take several steps to protect themselves following a data breach notification. This includes monitoring bank and credit card statements for unauthorized activity, placing fraud alerts on credit reports with all three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion), and reviewing their credit reports regularly for any suspicious activity. Consider changing passwords for all online accounts and enabling two-factor authentication wherever possible. It is also recommended to contact the company that experienced the breach and inquire about the specific data that was compromised and the support services offered.
Resources for Affected Employees
Several resources are available to help employees protect themselves. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) website offers valuable information and tools for victims of identity theft, including steps to take to report fraud and recover from identity theft. The three major credit bureaus also provide resources and tools to monitor credit reports and place fraud alerts. Additionally, many financial institutions offer identity theft protection services to their customers. These resources provide guidance and support to help navigate the complexities of recovering from a data breach.
Sample Communication Plan for Organizations
A clear and timely communication plan is essential for organizations to inform affected employees about the breach. This should include a prompt notification detailing the nature of the breach, the types of data compromised, and the steps employees should take to protect themselves. The organization should provide contact information for employees to seek assistance and offer resources such as credit monitoring services. Regular updates should be provided to keep employees informed about the ongoing investigation and any further actions being taken. Transparency and empathy are crucial in managing the situation effectively. A sample email or letter could Artikel the incident, explain the data involved, and offer a toll-free number and dedicated website for assistance.
The Role of Software Developers and Vendors
Source: cloudfront.net
The MoveIt data breach highlights a critical truth: secure software isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s a fundamental necessity. The responsibility for preventing vulnerabilities like the one exploited in MoveIt rests squarely on the shoulders of software developers and the vendors who release their products to the world. Their actions, or inactions, directly impact the security and privacy of countless users.
Software developers play a pivotal role in building secure systems. Their expertise in coding practices and understanding of security principles are crucial in preventing vulnerabilities from emerging in the first place. Vendors, in turn, are responsible for ensuring the software they distribute is thoroughly tested and patched against known vulnerabilities. The failure of either party can lead to catastrophic consequences, as we’ve seen with the MoveIt breach.
Responsibilities of Software Developers in Preventing Vulnerabilities
Secure coding practices are paramount. This includes adhering to established security principles like input validation, output encoding, and secure authentication mechanisms. Developers should be well-versed in common vulnerabilities and exploitation techniques, allowing them to proactively avoid introducing weaknesses into their code. Regular security training and code reviews are also essential, providing opportunities for peer feedback and the identification of potential security flaws before they reach production. Employing static and dynamic code analysis tools can automate the detection of vulnerabilities during the development process, catching many problems before they can be exploited.
Best Practices for Secure Coding and Vulnerability Management
Implementing robust vulnerability management is crucial. This involves establishing a structured process for identifying, reporting, and remediating security flaws. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be part of the development lifecycle, providing an independent assessment of the software’s security posture. Furthermore, adopting a “security by design” philosophy, where security is integrated into every stage of the development process, rather than being an afterthought, is vital. This includes carefully considering security implications at the design phase, not just during implementation. Finally, maintaining detailed documentation of the software’s architecture and security controls is essential for facilitating effective vulnerability management and incident response.
Comparison of Software Development Methodologies and Security
Different software development methodologies offer varying levels of built-in security. Agile methodologies, for example, emphasize iterative development and frequent feedback loops, which can help to identify and address security issues early in the development cycle. However, the rapid pace of Agile can sometimes compromise security if proper security practices aren’t strictly enforced. Waterfall methodologies, on the other hand, have a more structured approach, potentially allowing for more thorough security testing, but their rigidity can make it harder to adapt to newly discovered vulnerabilities. DevSecOps, which integrates security into every stage of the DevOps lifecycle, represents a more modern approach that aims to combine the speed of Agile with the security focus of more traditional methods. The choice of methodology should be tailored to the specific project and risk profile, with a strong emphasis on security regardless of the approach chosen.
Importance of Timely Security Updates and Patching Procedures
Timely patching is crucial in mitigating the risk of exploitation. Software vendors must establish efficient processes for identifying, developing, and deploying security updates. These updates should be communicated clearly to users, with instructions on how to apply them quickly and effectively. A well-defined patch management system, including automated update mechanisms where possible, is essential for minimizing the window of vulnerability. Ignoring or delaying security updates leaves systems exposed to known threats, creating a significant risk for data breaches and other security incidents. The MoveIt vulnerability underscores the critical need for vendors to prioritize prompt patching and effective communication with their users.
Process of Identifying, Reporting, and Addressing Software Vulnerabilities
The following flowchart illustrates the typical process:
[Imagine a flowchart here. It would begin with “Vulnerability Discovery” (e.g., through penetration testing, code review, user report). This would branch to “Vulnerability Verification” (confirming the existence and severity). This would lead to “Vulnerability Reporting” (internal reporting and potentially to external security agencies like CVE). Then, “Vulnerability Analysis” (determining the impact and potential solutions). Finally, “Vulnerability Remediation” (developing and deploying a patch) and “Verification of Fix” (testing the patch to ensure the vulnerability is resolved). The process would loop back to “Vulnerability Discovery” for ongoing monitoring.]
Legal and Regulatory Implications
The MoveIt data breach has significant legal and regulatory ramifications for the organizations involved, extending far beyond simple reputational damage. Understanding the complex web of laws and regulations governing data protection is crucial for assessing the potential liabilities and necessary responses. This section Artikels the key legal and regulatory frameworks at play, potential legal actions, and the variations in legal responses across different jurisdictions.
Relevant Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Data breaches like the MoveIt incident trigger a cascade of legal obligations under various frameworks. In the United States, laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – if protected health information was compromised – and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), along with its successor the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), are relevant depending on the location and type of data involved. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies if any EU citizens’ data was affected, imposing stringent requirements on data processing and breach notification. Other countries have their own data protection laws, leading to a complex jurisdictional landscape. For instance, the UK’s Data Protection Act 2018 mirrors some aspects of the GDPR. The specific legal framework applicable depends on the location of the affected individuals and the organizations involved.
Potential Legal Liabilities for Organizations
Organizations involved in the MoveIt breach face potential legal liabilities under various theories of liability. These include negligence, breach of contract, and violations of data protection laws. Negligence claims may arise if organizations failed to take reasonable steps to protect the data, such as failing to patch known vulnerabilities. Breach of contract claims could be brought by individuals or organizations whose contractual agreements stipulated certain data protection standards. Violations of data protection laws, like the GDPR or CCPA, can lead to substantial fines and penalties. The severity of the penalties varies depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the breach. For example, under the GDPR, fines can reach up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
Notification Requirements
Organizations have legal obligations to notify affected individuals and regulatory bodies about data breaches. The specifics of these notification requirements vary by jurisdiction. The GDPR mandates notification within 72 hours of becoming aware of a breach, while the CCPA requires notification without unreasonable delay. The notification must include details about the breach, the types of data affected, and steps individuals can take to mitigate potential harm. Failure to comply with notification requirements can lead to further penalties and legal actions. Regulatory bodies, such as the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in the UK or the California Attorney General’s office, have the power to investigate breaches and impose sanctions.
Comparison of Legal Responses Across Jurisdictions, Moveit 0 day employee data stolen
Legal responses to data breaches vary significantly across jurisdictions. The GDPR, for example, is known for its strict requirements and substantial penalties. Other jurisdictions, such as the United States, have a more patchwork approach to data protection, with varying state laws and federal regulations. This difference in legal frameworks can lead to inconsistencies in how data breaches are handled and the resulting legal consequences for organizations. A multinational organization with operations in multiple jurisdictions might face a complex and multifaceted legal response.
Potential Legal Actions
Several legal actions could be taken against the responsible parties in the MoveIt breach. These could include class-action lawsuits by affected individuals seeking compensation for damages, such as identity theft or financial loss. Regulatory bodies could also launch investigations, leading to fines and enforcement actions. Private lawsuits by businesses who suffered financial losses due to the breach are also possible. The specific legal actions taken will depend on the facts of the case, the applicable laws, and the evidence available. The outcome of these legal actions could have significant financial and reputational consequences for the organizations involved.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies: Moveit 0 Day Employee Data Stolen

Source: dailysocial.id
The MoveIt vulnerability highlighted a critical need for proactive security measures, not just reactive patching. Preventing future 0-day exploits requires a multi-layered approach encompassing robust development practices, proactive vulnerability management, and a strong security posture across the entire organization. This goes beyond simply installing security software; it’s about building a culture of security.
Preventing similar 0-day exploits demands a holistic strategy that addresses vulnerabilities throughout the software development lifecycle and extends to operational security. This includes rigorous code reviews, penetration testing, and continuous monitoring for suspicious activity. Furthermore, a well-defined incident response plan is crucial to minimize the impact of any successful breach.
Software Development Lifecycle Security
Secure coding practices are paramount. Developers should adhere to secure coding standards, prioritize input validation, and regularly undergo security training. Regular penetration testing and code reviews by independent security experts can uncover vulnerabilities before they’re exploited. Implementing static and dynamic application security testing (SAST and DAST) tools can automate the detection of common vulnerabilities. Regular updates and patching are also essential, ideally automated to ensure timely responses to newly discovered vulnerabilities. The adoption of a DevSecOps model, integrating security into every stage of the development process, is crucial for building secure software from the ground up. This involves automating security checks, incorporating security testing into CI/CD pipelines, and fostering a collaborative culture between developers and security teams.
Robust Security Measures to Minimize Breach Impact
Minimizing the impact of data breaches relies heavily on a strong security architecture. This includes data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network, robust access control mechanisms to limit who can access sensitive data, and regular backups of critical data to facilitate recovery in case of a breach. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Regular security awareness training for employees is crucial to educate them about phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other common attack vectors. Furthermore, a well-defined incident response plan, regularly tested and updated, ensures a coordinated and effective response to a security incident.
Comprehensive Security Plan for Organizations
A comprehensive security plan should incorporate several key elements. Firstly, a regular vulnerability assessment and penetration testing program is essential to identify and address weaknesses in the organization’s systems. This should be complemented by a robust incident response plan, detailing the steps to take in the event of a security breach. This plan should include communication protocols, data recovery procedures, and legal and regulatory compliance considerations. Regular security awareness training for employees is critical to reduce the risk of human error, a major factor in many breaches. Finally, strong access control policies, including least privilege access and multi-factor authentication, are vital to limit the potential damage from a compromised account. Regular audits and reviews of the security plan are essential to ensure its effectiveness and adapt to evolving threats.
Key Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Identifying key indicators of compromise (IOCs) related to the MoveIt vulnerability is crucial for early detection. These IOCs could include unusual network traffic patterns, such as a surge in connections to known command-and-control servers or suspicious outbound data transfers. Anomalous database activity, like a sudden increase in queries or modifications of sensitive data, would also be a significant indicator. Unexpected login attempts from unusual geographic locations or the use of compromised credentials should also raise suspicion. Furthermore, the presence of malicious files or processes related to the MoveIt vulnerability should be actively monitored. The timely detection of these IOCs can significantly reduce the impact of a successful attack.
Security Tools and Technologies
Several security tools and technologies can help prevent and detect attacks like the MoveIt vulnerability.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for malicious activity and can block or alert on suspicious patterns.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM solutions collect and analyze security logs from various sources to identify potential threats.
- Vulnerability Scanners: These tools automatically scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: DLP tools monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities on individual endpoints.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): WAFs protect web applications from attacks by filtering malicious traffic.
- Database Activity Monitoring (DAM): DAM solutions monitor database activity for suspicious behavior.
Final Conclusion
The MoveIt 0-day exploit serves as a stark reminder of the ever-evolving threat landscape in the digital age. The sheer scale of the data breach underscores the critical need for robust security measures, proactive vulnerability management, and a collaborative approach between developers, vendors, and users. While the immediate aftermath focuses on damage control and support for victims, the long-term impact will necessitate significant changes in software development practices, security protocols, and regulatory frameworks. The lessons learned from this incident are invaluable, pushing us to build a more secure and resilient digital future.





