Redline and meta infostealers: Sounds like something straight out of a cyberpunk thriller, right? Wrong. It’s a chilling reality in the world of cybersecurity. These sophisticated attacks are quietly stealing sensitive data from unsuspecting victims, leaving a trail of financial ruin and reputational damage in their wake. This deep dive explores the intricacies of these threats, from their underlying mechanisms to the strategies for detection and prevention. We’ll uncover the dark arts of social engineering, examine real-world examples of devastating breaches, and equip you with the knowledge to safeguard your digital assets.
We’ll dissect the techniques used to deploy meta infostealers, explore how they bypass security measures, and examine the devastating impact of successful attacks. Think compromised credentials, leaked financial information, and the potential for identity theft – the consequences are far-reaching and severe. But don’t worry, we’ll also delve into effective mitigation strategies, providing actionable steps to strengthen your defenses and minimize your risk.
Redline and Meta Infostealers

Source: slideplayer.com
The digital landscape is rife with threats, and two particularly insidious ones are Redline and meta infostealers. Understanding their functionalities and the relationship between them is crucial for bolstering cybersecurity defenses. This exploration delves into the definitions, mechanics, and distinctions between these malicious actors.
Redlining in Cybersecurity
In the context of cybersecurity, “redlining” doesn’t refer to discriminatory housing practices. Instead, it describes a technique used by threat actors to quickly and efficiently exfiltrate data from compromised systems. It often involves prioritizing the most valuable data—credentials, financial information, intellectual property—before moving on to less sensitive files. This focused approach maximizes the attacker’s return on investment (ROI) in terms of stolen information. Think of it as a highly efficient heist, targeting the crown jewels first.
Meta Infostealers: Functionality and Operation
A meta infostealer is a sophisticated piece of malware that goes beyond simply stealing data; it acts as a framework or platform for stealing various types of information. It typically operates by employing multiple modules or plugins, each designed to target specific data types. These modules might be focused on grabbing browser data (passwords, cookies, history), system information (hardware specifications, installed software), or files from specific locations (documents, images). The meta infostealer orchestrates these modules, collecting the data and often exfiltrating it to a command-and-control (C2) server controlled by the attacker. This modular design allows for flexibility and adaptability, making it difficult to detect and counter. Imagine it as a Swiss Army knife for data theft, capable of a wide range of malicious actions.
Comparison of Meta Infostealers
Different meta infostealers target different operating systems and employ various data exfiltration methods. Understanding these variations is key to effective detection and mitigation.
| Name | Target OS | Data Exfiltration Methods | Detection Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Meta Stealer A | Windows, macOS, Linux | HTTP POST, FTP, Email | Behavioral analysis, network monitoring, signature-based detection |
| Example Meta Stealer B | Windows | Encrypted communication channels, DNS tunneling | Anomaly detection, sandbox analysis, static analysis |
| Example Meta Stealer C | Windows, Android | Telegram, Discord bots | Monitoring suspicious network traffic, analyzing logs for unusual activity |
| Example Meta Stealer D | macOS | Cloud storage uploads | Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions, cloud access monitoring |
Relationship Between Redlining and Meta Infostealers
Redlining and meta infostealers often work hand-in-hand. Meta infostealers, with their ability to collect a wide array of data, provide the raw material for redlining. The attacker uses the meta infostealer to gather all available information, then employs redlining techniques to prioritize and extract the most valuable data first, maximizing their gains and minimizing the risk of detection. This coordinated approach increases the efficiency and effectiveness of the attack, making it more difficult to defend against. The meta infostealer provides the data, and redlining dictates the strategy for exfiltration.
Techniques Used in Redlining and Meta Infostealer Attacks: Redline And Meta Infostealers
Redlining and meta-infostealer attacks represent a sophisticated threat landscape, leveraging a combination of technical prowess and social manipulation to compromise systems and exfiltrate sensitive data. Understanding the techniques employed by attackers is crucial for effective defense. This section delves into the methods used to deploy meta infostealers, identify targets, bypass security, and exploit human vulnerabilities.
Meta infostealer deployment often begins with initial access, frequently achieved through phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links. These attachments might be disguised as legitimate documents, leading unsuspecting users to execute malicious code. Alternatively, attackers might exploit vulnerabilities in software or operating systems to gain unauthorized access. Once inside the network, the infostealer is deployed, often using techniques like PowerShell scripts or legitimate processes to mask its presence. The attacker then uses established command and control (C2) servers to manage the stolen data and maintain persistence on the compromised system.
Target System Identification and Redlining
Redlining, in this context, refers to the process of identifying and prioritizing valuable targets. Attackers use various techniques to identify systems containing sensitive information. This includes reconnaissance activities like network scanning to identify open ports and vulnerable services. They might also exploit publicly available information, such as company websites and social media, to gather intelligence about the target’s infrastructure and employees. Vulnerability scanners are frequently used to pinpoint weaknesses that can be exploited for initial access. The data gathered through this process is used to create a profile of the target, allowing attackers to focus their efforts on the most valuable systems.
Meta Infostealer Bypass Techniques
Meta infostealers employ various methods to bypass security measures. They might use techniques like process injection to hide their activity from security software. This involves injecting malicious code into a legitimate process, making it harder for security tools to detect the malicious activity. Additionally, attackers often use obfuscation techniques to make the code difficult to analyze and reverse engineer. This makes it harder for security researchers to understand how the malware operates and develop effective countermeasures. Finally, some infostealers utilize rootkit techniques to maintain persistence and evade detection.
Social Engineering in Meta Infostealer Attacks, Redline and meta infostealers
Social engineering plays a critical role in many meta-infostealer attacks. Attackers often leverage human psychology to trick victims into compromising their systems or revealing sensitive information. This can significantly increase the success rate of an attack.
- Phishing Emails: These emails often impersonate legitimate organizations or individuals, enticing recipients to click malicious links or open infected attachments.
- Pretexting: Attackers create a believable scenario to manipulate victims into divulging information. For example, they might pretend to be technical support and ask for remote access to a computer.
- Baiting: Attackers offer something desirable, such as a free gift or software, to lure victims into a trap.
- Quid Pro Quo: Attackers offer a service or favor in exchange for sensitive information.
- Tailgating: Attackers physically follow authorized personnel into restricted areas.
Impact and Consequences of Redlining and Meta Infostealer Breaches
Redlining and meta-infostealer attacks represent a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike, resulting in substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. The insidious nature of these attacks, often going undetected for extended periods, amplifies their destructive potential. Understanding the consequences is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation strategies.
The severity of the impact depends on several factors, including the sophistication of the attack, the volume of data compromised, and the organization’s response capabilities. However, certain common consequences consistently emerge across various incidents.
Real-World Incidents Involving Redlining and Meta Infostealers
Several high-profile incidents highlight the devastating impact of redlining and meta-infostealer attacks. For instance, the 2021 SolarWinds supply chain attack involved a sophisticated meta-infostealer that compromised numerous organizations, including government agencies and private companies. The attackers gained access to sensitive data, including internal communications and intellectual property, causing significant financial and reputational damage. Another example is the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, which leveraged a sophisticated redlining technique to spread rapidly across networks, crippling businesses worldwide and resulting in billions of dollars in losses. While not strictly a meta-infostealer, its widespread impact showcases the destructive potential of advanced redlining techniques. These attacks demonstrate the real-world consequences of insufficient security measures and highlight the need for proactive threat detection and response strategies.
Types of Data Commonly Stolen by Meta Infostealers
Meta infostealers are designed to collect a wide range of sensitive data. This typically includes credentials such as usernames and passwords, credit card information, personally identifiable information (PII) like names, addresses, and social security numbers, intellectual property, and confidential business documents. The breadth of data collected makes these attacks particularly dangerous, as the stolen information can be used for various malicious purposes, including identity theft, financial fraud, and corporate espionage. The indiscriminate nature of these attacks underscores the importance of robust data protection measures and comprehensive security protocols.
Financial and Reputational Damage Caused by These Attacks
The financial consequences of redlining and meta-infostealer breaches can be catastrophic. Organizations face direct costs associated with incident response, including investigation, remediation, legal fees, and notification costs. Indirect costs can be even more significant, encompassing lost productivity, damage to brand reputation, and decreased customer trust. Reputational damage can be long-lasting, impacting future business opportunities and investor confidence. The loss of sensitive data can lead to significant financial penalties and legal actions, further exacerbating the overall financial burden. For example, a breach exposing customer data could lead to hefty fines under regulations like GDPR.
Legal Ramifications for Organizations Affected by Breaches
Organizations facing redlining and meta-infostealer breaches face a complex web of legal ramifications. Data breach notification laws, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, mandate timely disclosure of data breaches to affected individuals and regulatory authorities. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and legal penalties. Furthermore, organizations may face lawsuits from individuals whose data was compromised, leading to significant legal costs and potential settlements. Compliance with data protection regulations is paramount in mitigating legal risks and minimizing the consequences of a breach. The legal landscape surrounding data security is constantly evolving, emphasizing the need for organizations to stay informed and adapt their security practices accordingly.
Detection and Prevention Strategies

Source: pcmag.com
Redlining and meta infostealer attacks represent a significant threat to both individual users and organizations. A robust security posture, encompassing proactive measures and rapid response capabilities, is crucial for mitigating these risks. This section Artikels a comprehensive strategy, encompassing preventative technologies, detection methods, and incident response procedures.
A multi-layered approach is essential for effective protection. This includes strengthening endpoint security, implementing robust network defenses, and educating users about phishing and social engineering tactics. Regular security audits and penetration testing can further identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them. The following sections detail key components of this strategy.
Security Tools and Technologies
Employing a suite of security tools is vital for detecting and preventing redlining and meta infostealer attacks. These tools provide various layers of defense, from network-level protection to endpoint monitoring and threat hunting. A layered approach significantly reduces the attack surface and enhances overall security.
Effective tools include advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and anti-malware software. Network segmentation can also limit the impact of a successful breach by isolating compromised systems. Regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing should be conducted to proactively identify and address weaknesses in the system.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Implementation
EDR solutions are paramount in detecting and responding to redlining and meta infostealer attacks. These solutions monitor endpoint activity for suspicious behavior, providing real-time alerts and enabling rapid incident response. Effective implementation requires careful configuration and integration with other security tools.
Key aspects of EDR implementation include: centralized management for efficient monitoring and response across multiple endpoints; real-time threat detection and alerting; forensic capabilities to investigate suspicious activity; and integration with other security tools for a comprehensive security posture. Regular updates and tuning of the EDR system are also critical for maintaining its effectiveness.
Incident Response to Meta Infostealer Attacks
A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of a successful meta infostealer attack. A swift and coordinated response can limit data exfiltration and prevent further damage. The following steps Artikel a typical incident response process.
The response should follow a structured methodology. The steps involved include: 1) Identification: Detecting the attack through security monitoring tools or user reports. 2) Containment: Isolating affected systems to prevent further compromise. 3) Eradication: Removing the malware and restoring affected systems to a clean state. 4) Recovery: Restoring data from backups and resuming normal operations. 5) Post-Incident Activity: Analyzing the attack to identify vulnerabilities and improve security measures. Documentation throughout the entire process is essential for future analysis and improvement.
Advanced Techniques and Emerging Threats
The landscape of cybercrime is constantly evolving, with meta infostealers and redlining techniques becoming increasingly sophisticated. Attackers are leveraging advanced evasion tactics and exploiting emerging vulnerabilities to bypass security measures and achieve their malicious goals. Understanding these advancements is crucial for effective defense.
Meta infostealers, in particular, are demonstrating a remarkable capacity for adaptation. They’re moving beyond simple data exfiltration to incorporate advanced techniques designed to evade detection and analysis. This includes the use of polymorphic code, which changes its structure to avoid signature-based detection, and the integration of anti-analysis techniques to hinder reverse engineering efforts. Redlining attacks, while less sophisticated in their core methodology, are increasingly combined with other attack vectors, creating a more complex and challenging threat.
Advanced Evasion Techniques Employed by Meta Infostealers
Meta infostealers are employing a range of sophisticated evasion techniques to avoid detection. These include techniques like process injection, where the malware injects its code into legitimate processes to mask its presence, and rootkit functionalities, which hide the malware’s files and registry entries. Furthermore, the use of encrypted communication channels makes it difficult to intercept and analyze the stolen data. The adoption of obfuscation techniques, such as code virtualization and packing, further complicates analysis and identification. These methods significantly increase the difficulty of detection and response.
Emerging Trends in Redlining and Meta Infostealer Attacks
Several emerging trends are shaping the threat landscape. One significant trend is the increasing use of automation. Attackers are leveraging automated tools and scripts to scale their operations, increasing the speed and efficiency of attacks. Another concerning trend is the convergence of redlining and meta infostealer attacks. Attackers may use redlining to identify high-value targets and then deploy meta infostealers to extract sensitive information. This combination amplifies the impact of the attack. The use of legitimate software and services for malicious purposes, a technique known as living off the land (LotL), is also becoming increasingly prevalent, making detection more challenging.
Comparison of Detection Method Effectiveness
Understanding the effectiveness of different detection methods is crucial for building robust defenses. The following table compares several common methods:
| Method | Effectiveness | Limitations | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signature-based detection | Moderate; effective against known threats | Ineffective against polymorphic malware and zero-day exploits; requires constant updates | Low to moderate |
| Behavioral analysis | High; detects malicious activities regardless of signature | Can generate false positives; requires sophisticated analysis tools | Moderate to high |
| Sandboxing | High; allows safe analysis of suspicious files | Can be bypassed by sophisticated malware; computationally expensive | Moderate to high |
| Threat intelligence feeds | Moderate; provides early warning of emerging threats | Relies on timely and accurate intelligence; may not cover all threats | Low to moderate |
Future Evolution of Redlining and Meta Infostealer Threats
The future evolution of these threats points towards even greater sophistication and automation. We can expect to see an increase in the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) by both attackers and defenders. Attackers will likely use AI to automate the discovery of vulnerabilities and to develop more evasive malware. Defenders, in turn, will need to leverage AI and ML to improve detection and response capabilities. The use of serverless architectures and cloud-based infrastructure will also likely play a significant role, both in enabling attacks and in providing opportunities for defense. For example, the NotPetya ransomware attack, while not directly a meta infostealer or redlining attack, demonstrated the devastating potential of sophisticated attacks leveraging legitimate infrastructure. The future will likely see more such attacks leveraging readily available cloud services and APIs.
Wrap-Up
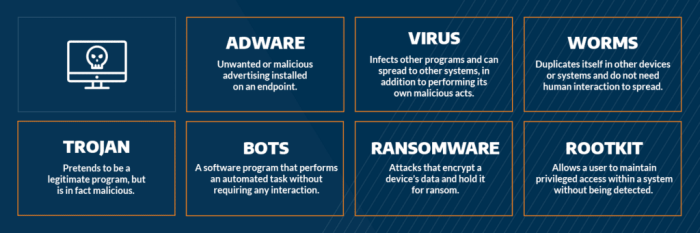
Source: arcticwolf.com
Redline and meta infostealer attacks are a serious threat, but understanding their mechanisms and employing proactive security measures can significantly reduce your vulnerability. From strengthening your endpoint security to implementing robust incident response plans, a multi-layered approach is key. Remember, staying informed about emerging threats and adapting your security strategy accordingly is crucial in this ever-evolving digital landscape. Don’t become another statistic – take control of your cybersecurity today.





